"V体育官网" Screening of long non-coding RNA and TUG1 inhibits proliferation with TGF-β induction in patients with COPD
- PMID: 27932875
- PMCID: PMC5135066
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S109570
Screening of long non-coding RNA and TUG1 inhibits proliferation with TGF-β induction in patients with COPD
"VSports手机版" Abstract
Objective: To evaluate differentially expressed long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and the potential role of lncRNA TUG1 in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) VSports手机版. .
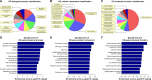
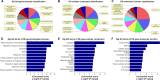
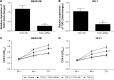
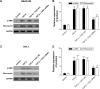
Methods: Total RNA was extracted from both COPD and non-COPD lung tissues, and microarray analysis was performed with 25,628 lncRNA probes and 20,106 mRNA probes. In addition, five up-regulated and five down-regulated lncRNAs were selected for identification using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. COPD cell model was established by transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) treatment. Cell Counting Kit-8 assay was used to detect BEAS-2B and HFL1 cell proliferation after TUG-siRNA transfection with TGF-β treatment. In addition, the expression levels of α-SMA and fibronectin proteins were determined using Western blot in BEAS-2B and HFL1 cells after TUG-siRNA transfection with TGF-β treatment. V体育安卓版.
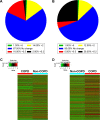
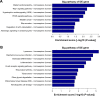
Results: There were 8,376 (32. 7%) differentially expressed lncRNAs and 5,094 (25. 3%) differentially expressed mRNAs in COPD lung tissues compared with non-COPD lung tissues V体育ios版. Five of the analyzed lncRNAs (BC038205, BC130595, TUG1, MEG3, and LOC646329) were markedly increased, while five lncRNAs (LOC729178, PLAC2, LOC339529, LINC00229, and SNHG5) were significantly decreased in COPD lung tissues compared with non-COPD lung tissues (n=20) (***P<0. 001). Knockdown of lncRNA TUG1 promotes BEAS-2B and HFL1 cell proliferation after TGF-β treatment through inhibiting the expression levels of α-SMA and fibronectin. .
Conclusion: Abundant, differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs were identified by microarray analysis and these might play a partial or key role in the diagnosis of patients with COPD. LncRNA TUG1 may become a very important class of biomarker and may act as a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for patients with COPD. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: COPD; TGF-β; lncRNA TUG1; long noncoding RNA; microarray analysis. V体育平台登录.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS, GOLD Scientific Committee Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(5):1256–1276. - PubMed
-
- Pauwels RA, Rabe KF. Burden and clinical features of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Lancet. 2004;364(9434):613–620. - PubMed (V体育官网)
-
- Demedts IK, Brusselle GG, Bracke KR, Vermaelen KY, Pauwels RA. Matrix metalloproteinases in asthma and COPD. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5(3):257–263. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Barnes PJ, Shapiro SD, Pauwels RA. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: molecular and cellularmechanisms. Eur Respir J. 2003;22(4):672–688. - PubMed
"V体育官网入口" MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
VSports手机版 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

