Altered Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs in Blood After Ischemic Stroke and Proximity to Putative Stroke Risk Loci
- PMID: 27834745
- PMCID: V体育官网 - PMC5127755
- DOI: "VSports手机版" 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013869
Altered Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs in Blood After Ischemic Stroke and Proximity to Putative Stroke Risk Loci
Abstract (VSports注册入口)
Background and purpose: Although peripheral blood mRNA and micro-RNA change after ischemic stroke, any role for long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), which comprise most of the genome and have been implicated in various diseases, is unknown VSports手机版. Thus, we hypothesized that lncRNA expression also changes after stroke. .
Methods: lncRNA expression was assessed in 266 whole-blood RNA samples drawn once per individual from patients with ischemic stroke and matched with vascular risk factor controls. Differential lncRNA expression was assessed by ANCOVA (P<0. 005; fold change>|1. 2|), principal components analysis, and hierarchical clustering on a derivation set (n=176) and confirmed on a validation set (n=90). Poststroke temporal lncRNA expression changes were assessed using ANCOVA with confounding factor correction (P<0. 005; partial correlation with time since event >|0. 4|) V体育安卓版. Because sexual dimorphism exists in stroke, analyses were performed for each sex separately. .
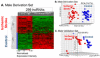
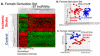
Results: A total of 299 lncRNAs were differentially expressed between stroke and control males, whereas 97 lncRNAs were differentially expressed between stroke and control females V体育ios版. Significant changes of lncRNA expression with time after stroke were detected for 49 lncRNAs in men and 31 lncRNAs in women. Some differentially expressed lncRNAs mapped close to genomic locations of previously identified putative stroke-risk genes, including lipoprotein, lipoprotein(a)-like 2, ABO (transferase A, α1-3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase; transferase B, α1-3-galactosyltransferase) blood group, prostaglandin 12 synthase, and α-adducins. .
Conclusions: This study provides evidence of altered and sexually dimorphic lncRNA expression in peripheral blood of patients with stroke compared with that of controls and suggests that lncRNAs have potential for stroke biomarker development VSports最新版本. Some regulated lncRNA could regulate some previously identified putative stroke-risk genes. .
Keywords: RNA, long noncoding; RNA, untranslated; gene expression; risk factor; stroke. V体育平台登录.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Stamova B, Tian Y, Jickling G, Bushnell C, Zhan X, Liu D, et al. The x-chromosome has a different pattern of gene expression in women compared with men with ischemic stroke. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 2012;43:326–334. - "VSports在线直播" PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
VSports手机版 - Substances
"V体育官网" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
VSports - Full Text Sources
V体育ios版 - Other Literature Sources
Medical

