Fbxw7 Deletion Accelerates KrasG12D-Driven Pancreatic Tumorigenesis via Yap Accumulation
- PMID: 27764699
- PMCID: PMC5071541
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2016.08.009
Fbxw7 Deletion Accelerates KrasG12D-Driven Pancreatic Tumorigenesis via Yap Accumulation
Abstract
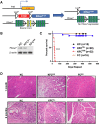
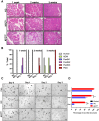
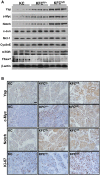
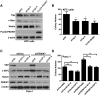
Pancreatic cancers driven by KRAS mutations require additional mutations for tumor progression. The tumor suppressor FBXW7 is altered in pancreatic cancers, but its contribution to pancreatic tumorigenesis is unknown. To determine potential cooperation between Kras mutation and Fbxw7 inactivation in pancreatic tumorigenesis, we generated P48-Cre;LSL-KrasG12D;Fbxw7fl/fl (KFCfl/fl) compound mice. We found that KFCfl/fl mice displayed accelerated tumorigenesis: all mice succumbed to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) by 40 days of age, with PDA onset occurring by 2 weeks of age. PDA in KFCfl/fl mice was preceded by earlier onset of acinar-to-ductal metaplasia (ADM) and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) lesions, and associated with chromosomal instability and the accumulation of Fbxw7 substrates Yes-associated protein (Yap), c-Myc, and Notch VSports手机版. Using KFCfl/fl and FBXW7-deficient human pancreatic cancer cells, we found that Yap silencing attenuated growth promotion by Fbxw7 deletion. Our data demonstrate that Fbxw7 is a potent suppressor of KrasG12D-induced pancreatic tumorigenesis due, at least in part, to negative regulation of Yap. .
Copyright © 2016 The Authors V体育安卓版. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. .
Figures
References
-
- Rozenblum E, Schutte M, Goggins M, Hahn SA, Panzer S, Zahurak M, Goodman SN, Sohn TA, Hruban RH, Yeo CJ. Tumor-suppressive pathways in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1997;57:1731–1734. - PubMed
-
- Hingorani SR, Petricoin EF, Maitra A, Rajapakse V, King C, Jacobetz MA, Ross S, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Hitt BA. Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:437–450. - PubMed
-
- Collins MA, Bednar F, Zhang Y, Brisset JC, Galban S, Galban CJ, Rakshit S, Flannagan KS, Adsay NV, Pasca di Magliano M. Oncogenic Kras is required for both the initiation and maintenance of pancreatic cancer in mice. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:639–653. - PMC (V体育ios版) - PubMed
MeSH terms
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
Substances
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous (VSports注册入口)

