The Phylogeny and Active Site Design of Eukaryotic Copper-only Superoxide Dismutases
- PMID: 27535222
- PMCID: PMC5076504 (V体育平台登录)
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.748251
The Phylogeny and Active Site Design of Eukaryotic Copper-only Superoxide Dismutases
Abstract
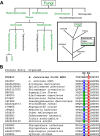
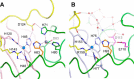
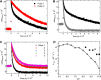
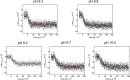
In eukaryotes the bimetallic Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzymes play important roles in the biology of reactive oxygen species by disproportionating superoxide anion. Recently, we reported that the fungal pathogen Candida albicans expresses a novel copper-only SOD, known as SOD5, that lacks the zinc cofactor and electrostatic loop (ESL) domain of Cu/Zn-SODs for substrate guidance. Despite these abnormalities, C VSports手机版. albicans SOD5 can disproportionate superoxide at rates limited only by diffusion. Here we demonstrate that this curious copper-only SOD occurs throughout the fungal kingdom as well as in phylogenetically distant oomycetes or "pseudofungi" species. It is the only form of extracellular SOD in fungi and oomycetes, in stark contrast to the extracellular Cu/Zn-SODs of plants and animals. Through structural biology and biochemical approaches we demonstrate that these copper-only SODs have evolved with a specialized active site consisting of two highly conserved residues equivalent to SOD5 Glu-110 and Asp-113. The equivalent positions are zinc binding ligands in Cu/Zn-SODs and have evolved in copper-only SODs to control catalysis and copper binding in lieu of zinc and the ESL. Similar to the zinc ion in Cu/Zn-SODs, SOD5 Glu-110 helps orient a key copper-coordinating histidine and extends the pH range of enzyme catalysis. SOD5 Asp-113 connects to the active site in a manner similar to that of the ESL in Cu/Zn-SODs and assists in copper cofactor binding. Copper-only SODs are virulence factors for certain fungal pathogens; thus this unique active site may be a target for future anti-fungal strategies. .
Keywords: copper; enzyme; fungi; superoxide dismutase (SOD); superoxide ion; x-ray crystallography. V体育安卓版.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. V体育ios版.
Figures


References
-
- McCord J. M., and Fridovich I. (1969) Superoxide dismutase an enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J. Biol. Chem. 244, 6049–6055 - PubMed
-
- Abreu I. A., and Cabelli D. E. (2010) Superoxide dismutases: a review of the metal-associated mechanistic variations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1804, 263–274 - PubMed
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
Associated data (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育官网入口)
Other Literature Sources

