Induced superficial chondrocyte death reduces catabolic cartilage damage in murine posttraumatic osteoarthritis
- PMID: 27427985
- PMCID: PMC4966316
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI83676
Induced superficial chondrocyte death reduces catabolic cartilage damage in murine posttraumatic osteoarthritis
Abstract
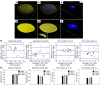
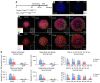
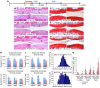
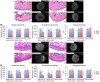
Joints that have degenerated as a result of aging or injury contain dead chondrocytes and damaged cartilage. Some studies have suggested that chondrocyte death precedes cartilage damage, but how the loss of chondrocytes affects cartilage integrity is not clear. In this study, we examined whether chondrocyte death undermines cartilage integrity in aging and injury using a rapid 3D confocal cartilage imaging technique coupled with standard histology. We induced autonomous expression of diphtheria toxin to kill articular surface chondrocytes in mice and determined that chondrocyte death did not lead to cartilage damage. Moreover, cartilage damage after surgical destabilization of the medial meniscus of the knee was increased in mice with intact chondrocytes compared with animals whose chondrocytes had been killed, suggesting that chondrocyte death does not drive cartilage damage in response to injury. These data imply that chondrocyte catabolism, not death, contributes to articular cartilage damage following injury VSports手机版. Therefore, therapies targeted at reducing the catabolic phenotype may protect against degenerative joint disease. .
Figures
References
-
- Pearle AD, Warren RF, Rodeo SA. Basic science of articular cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin Sports Med. 2005;24(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.csm.2004.08.007. - DOI (V体育ios版) - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter JA, Mankin HJ, Grodzinsky AJ. Articular cartilage and osteoarthritis. Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:465–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

