Interconnected microbiomes and resistomes in low-income human habitats
- PMID: 27172044
- PMCID: V体育官网入口 - PMC4869995
- DOI: 10.1038/nature17672
Interconnected microbiomes and resistomes in low-income human habitats (V体育官网)
"VSports在线直播" Abstract
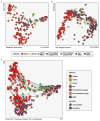
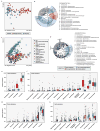
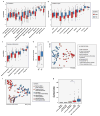
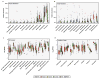
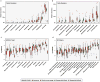
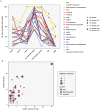
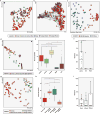
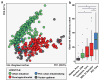
Antibiotic-resistant infections annually claim hundreds of thousands of lives worldwide. This problem is exacerbated by exchange of resistance genes between pathogens and benign microbes from diverse habitats. Mapping resistance gene dissemination between humans and their environment is a public health priority. Here we characterized the bacterial community structure and resistance exchange networks of hundreds of interconnected human faecal and environmental samples from two low-income Latin American communities. We found that resistomes across habitats are generally structured by bacterial phylogeny along ecological gradients, but identified key resistance genes that cross habitat boundaries and determined their association with mobile genetic elements VSports手机版. We also assessed the effectiveness of widely used excreta management strategies in reducing faecal bacteria and resistance genes in these settings representative of low- and middle-income countries. Our results lay the foundation for quantitative risk assessment and surveillance of resistance gene dissemination across interconnected habitats in settings representing over two-thirds of the world's population. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures

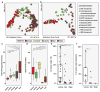
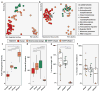

References
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance. 1. World Health Organization; 2014.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013. 2013.
-
- The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, C. b. J. O. N. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. 2014;2014
-
- Forsberg KJ, et al. The shared antibiotic resistome of soil bacteria and human pathogens. Science. 2012;337:1107–1111. doi: 10.1126/science.1220761. - "VSports最新版本" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
"VSports app下载" Grants and funding
"V体育官网入口" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

