Neutrophil extracellular traps - the dark side of neutrophils
- PMID: 27135878
- PMCID: PMC4855925
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI84538
Neutrophil extracellular traps - the dark side of neutrophils
Abstract (V体育ios版)
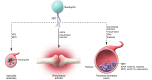
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) were discovered as extracellular strands of decondensed DNA in complex with histones and granule proteins, which were expelled from dying neutrophils to ensnare and kill microbes VSports手机版. NETs are formed during infection in vivo by mechanisms different from those originally described in vitro. Citrullination of histones by peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4) is central for NET formation in vivo. NETs may spur formation of autoantibodies and may also serve as scaffolds for thrombosis, thereby providing a link among infection, autoimmunity, and thrombosis. In this review, we present the mechanisms by which NETs are formed and discuss the physiological and pathophysiological consequences of NET formation. We conclude that NETs may be of more importance in autoimmunity and thrombosis than in innate immune defense. .
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
V体育2025版 - Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports" Other Literature Sources
Medical

