Inflammatory cytokines induce caveolin-1/β-catenin signalling in rat nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through the p38 MAPK pathway
- PMID: 27125453
- PMCID: "VSports注册入口" PMC6496863
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12254
Inflammatory cytokines induce caveolin-1/β-catenin signalling in rat nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through the p38 MAPK pathway
Abstract
Objectives: Apoptosis of nucleus pulposus (NP) cells is a major cause of intervertebral disc degeneration. To elucidate relationships between caveolin-1 and cytokine-induced apoptosis, we investigated the role of caveolin-1 in cytokine-induced apoptosis in rat NP cells and the related signalling pathway. VSports手机版.
Materials and methods: Rat NP cells were treated with interleukin (IL)-1β or tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and knockdown of caveolin-1 and β-catenin was achieved using specific siRNAs. Then, apoptotic level of rat NP cells and expression and activation of caveolin-1/β-catenin signalling were assessed by flow cytometric analysis, qRT-PCR, western blotting and luciferase assays V体育安卓版. The relationship between the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and caveolin-1 promoter activity was also determined by luciferase assays. .
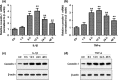
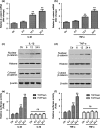
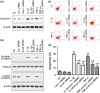
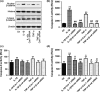
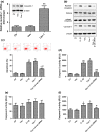
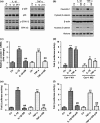
Results: IL-1β and TNF-α induced apoptosis, upregulated caveolin-1 expression and activated Wnt/β-catenin signalling in rat NP cells, while the induction effect of cytokines was reversed by caveolin-1 siRNA and β-catenin siRNA. Promotion of rat NP cell apoptosis and nuclear translocation of β-catenin induced by caveolin-1 overexpression were abolished by β-catenin siRNA V体育ios版. Furthermore, pretreatment with a p38 MAPK inhibitor or dominant negative-p38, blocked cytokine-dependent induction of caveolin-1/β-catenin expression and activity. .
Conclusions: The results revealed the role of p38/caveolin-1/β-catenin in inflammatory cytokine-induced apoptosis in rat NP cells. Thus, controlling p38/caveolin-1/β-catenin activity seemed to regulate IL-1β- and TNF-α-induced apoptosis in the NP during intervertebral disc degeneration. VSports最新版本.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
"VSports app下载" Figures
References
-
- Katz JN (2006) Lumbar disc disorders and low‐back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 88(Suppl 2), 21–24. - PubMed
-
- Hadjipavlou AG, Tzermiadianos MN, Bogduk N, Zindrick MR (2008) The pathophysiology of disc degeneration: a critical review. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 90, 1261–1270. - PubMed
-
- Ding F, Shao ZW, Xiong LM (2013) Cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration. Apoptosis 18, 777–785. - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
-
- Aguiar DJ, Johnson SL, Oegema TR (1999) Notochordal cells interact with nucleus pulposus cells: regulation of proteoglycan synthesis. Exp. Cell Res. 246, 129–137. - PubMed
MeSH terms (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
"VSports在线直播" Associated data
- Actions (V体育官网)
LinkOut - more resources (VSports)
"V体育2025版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

