Transcription factor KLF2 regulates homeostatic NK cell proliferation and survival
- PMID: 27114551
- PMCID: PMC4868471
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1521491113
Transcription factor KLF2 regulates homeostatic NK cell proliferation and survival (V体育ios版)
VSports app下载 - Abstract
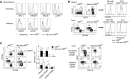
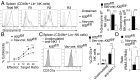
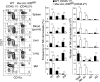
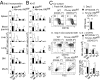
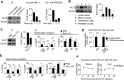
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphocytes that recognize and lyse virally infected or transformed cells. This latter property is being pursued in clinics to treat leukemia with the hope that further breakthroughs in NK cell biology can extend treatments to other cancers VSports手机版. At issue is the ability to expand transferred NK cells and prolong their functionality within the context of a tumor. In terms of NK cell expansion and survival, we now report that Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) is a key transcription factor that underpins both of these events. Excision of Klf2 using gene-targeted mouse models promotes spontaneous proliferation of immature NK cells in peripheral tissues, a phenotype that is replicated under ex vivo conditions. Moreover, KLF2 imprints a homeostatic migration pattern on mature NK cells that allows these cells to access IL-15-rich microenvironments. KLF2 accomplishes this feat within the mature NK cell lineage via regulation of a subset of homing receptors that respond to homeostatic ligands while leaving constitutively expressed receptors that recognize inflammatory cytokines unperturbed. Under steady-state conditions, KLF2-deficient NK cells alter their expression of homeostatic homing receptors and subsequently undergo apoptosis due to IL-15 starvation. This novel mechanism has implications regarding NK cell contraction following the termination of immune responses including the possibility that retention of an IL-15 transpresenting support system is key to extending NK cell activity in a tumor environment. .
Keywords: IL-15; KLF2; NK cell; NK cell homeostasis; NK cell proliferation V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References (VSports最新版本)
-
- Miller JS, et al. Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of human haploidentical NK cells in patients with cancer. Blood. 2005;105(8):3051–3057. - PubMed
-
- Walzer T, Vivier E. G-protein-coupled receptors in control of natural killer cell migration. Trends Immunol. 2011;32(10):486–492. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
MeSH terms (V体育2025版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Substances
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Grants and funding (V体育官网)
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育官网" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

