Identification of additional risk loci for stroke and small vessel disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 27068588
- PMCID: PMC4943223 (VSports在线直播)
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00102-2
Identification of additional risk loci for stroke and small vessel disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies (V体育安卓版)
Abstract
Background: Genetic determinants of stroke, the leading neurological cause of death and disability, are poorly understood and have seldom been explored in the general population. Our aim was to identify additional loci for stroke by doing a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies VSports手机版. .
Methods: For the discovery sample, we did a genome-wide analysis of common genetic variants associated with incident stroke risk in 18 population-based cohorts comprising 84 961 participants, of whom 4348 had stroke. Stroke diagnosis was ascertained and validated by the study investigators. Mean age at stroke ranged from 45·8 years to 76·4 years, and data collection in the studies took place between 1948 and 2013. We did validation analyses for variants yielding a significant association (at p<5 × 10(-6)) with all-stroke, ischaemic stroke, cardioembolic ischaemic stroke, or non-cardioembolic ischaemic stroke in the largest available cross-sectional studies (70 804 participants, of whom 19 816 had stroke) V体育安卓版. Summary-level results of discovery and follow-up stages were combined using inverse-variance weighted fixed-effects meta-analysis, and in-silico lookups were done in stroke subtypes. For genome-wide significant findings (at p<5 × 10(-8)), we explored associations with additional cerebrovascular phenotypes and did functional experiments using conditional (inducible) deletion of the probable causal gene in mice. We also studied the expression of orthologs of this probable causal gene and its effects on cerebral vasculature in zebrafish mutants. .
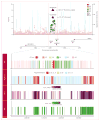
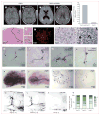
Findings: We replicated seven of eight known loci associated with risk for ischaemic stroke, and identified a novel locus at chromosome 6p25 (rs12204590, near FOXF2) associated with risk of all-stroke (odds ratio [OR] 1·08, 95% CI 1·05-1·12, p=1·48 × 10(-8); minor allele frequency 21%). The rs12204590 stroke risk allele was also associated with increased MRI-defined burden of white matter hyperintensity-a marker of cerebral small vessel disease-in stroke-free adults (n=21 079; p=0·0025) V体育ios版. Consistently, young patients (aged 2-32 years) with segmental deletions of FOXF2 showed an extensive burden of white matter hyperintensity. Deletion of Foxf2 in adult mice resulted in cerebral infarction, reactive gliosis, and microhaemorrhage. The orthologs of FOXF2 in zebrafish (foxf2b and foxf2a) are expressed in brain pericytes and mutant foxf2b(-/-) cerebral vessels show decreased smooth muscle cell and pericyte coverage. .
Interpretation: We identified common variants near FOXF2 that are associated with increased stroke susceptibility. Epidemiological and experimental data suggest that FOXF2 mediates this association, potentially via differentiation defects of cerebral vascular mural cells VSports最新版本. Further expression studies in appropriate human tissues, and further functional experiments with long follow-up periods are needed to fully understand the underlying mechanisms. .
Funding: NIH, NINDS, NHMRC, CIHR, European national research institutions, Fondation Leducq V体育平台登录. .
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. VSports注册入口.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
V体育ios版 - Comment in
-
A stroke of insight from genetics.Lancet Neurol. 2016 Jun;15(7):653-654. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30028-X. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Lancet Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27068587 No abstract available.
VSports - References
-
- Johnston SC, Mendis S, Mathers CD. Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: estimates from monitoring, surveillance, and modelling. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:345–54. - PubMed
-
- Falcone GJ, Malik R, Dichgans M, Rosand J. Current concepts and clinical applications of stroke genetics. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:405–18. - PubMed
-
- Bevan S, Traylor M, Adib-Samii P, et al. Genetic heritability of ischemic stroke and the contribution of previously reported candidate gene and genomewide associations. Stroke. 2012;43:3161–67. - PubMed
-
- Manolio TA. Bringing genome-wide association findings into clinical use. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:549–58. - PubMed (V体育安卓版)
"VSports手机版" Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Grants and funding
- G1001799/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States (V体育官网)
- 095626/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N01104X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- V体育2025版 - U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States (VSports)
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- "V体育平台登录" R01 AG008122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- VSports最新版本 - R01 HL088521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

