The Terminal Oxidase Cytochrome bd Promotes Sulfide-resistant Bacterial Respiration and Growth
- PMID: 27030302
- PMCID: "V体育平台登录" PMC4815019
- DOI: VSports最新版本 - 10.1038/srep23788
V体育2025版 - The Terminal Oxidase Cytochrome bd Promotes Sulfide-resistant Bacterial Respiration and Growth
Abstract
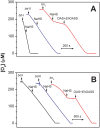
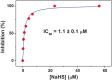
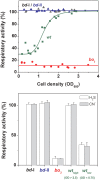
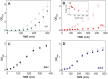
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) impairs mitochondrial respiration by potently inhibiting the heme-copper cytochrome c oxidase. Since many prokaryotes, including Escherichia (E. ) coli, generate H2S and encounter high H2S levels particularly in the human gut, herein we tested whether bacteria can sustain sulfide-resistant O2-dependent respiration. E. coli has three respiratory oxidases, the cyanide-sensitive heme-copper bo3 enzyme and two bd oxidases much less sensitive to cyanide. Working on the isolated enzymes, we found that, whereas the bo3 oxidase is inhibited by sulfide with half-maximal inhibitory concentration IC50 = 1 VSports手机版. 1 ± 0. 1 μM, under identical experimental conditions both bd oxidases are insensitive to sulfide up to 58 μM. In E. coli respiratory mutants, both O2-consumption and aerobic growth proved to be severely impaired by sulfide when respiration was sustained by the bo3 oxidase alone, but unaffected by ≤200 μM sulfide when either bd enzyme acted as the only terminal oxidase. Accordingly, wild-type E. coli showed sulfide-insensitive respiration and growth under conditions favouring the expression of bd oxidases. In all tested conditions, cyanide mimicked the functional effect of sulfide on bacterial respiration. We conclude that bd oxidases promote sulfide-resistant O2-consumption and growth in E. coli and possibly other bacteria. The impact of this discovery is discussed. .
Figures
References
-
- Wallace J. L. & Wang R. Hydrogen sulfide-based therapeutics: exploiting a unique but ubiquitous gasotransmitter. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 14, 329–345 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Nicholls P., Marshall D. C., Cooper C. E. & Wilson M. T. Sulfide inhibition of and metabolism by cytochrome c oxidase. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 41, 1312–1316 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Cooper C. E. & Brown G. C. The inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase by the gases carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, hydrogen cyanide and hydrogen sulfide: chemical mechanism and physiological significance. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 40, 533–539 (2008). - PubMed (V体育安卓版)
Publication types
MeSH terms (VSports在线直播)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Substances
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
V体育2025版 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
VSports app下载 - Molecular Biology Databases

