"V体育安卓版" Mortality prediction in patients with severe septic shock: a pilot study using a target metabolomics approach
- PMID: 26847922
- PMCID: PMC4742912
- DOI: VSports在线直播 - 10.1038/srep20391
Mortality prediction in patients with severe septic shock: a pilot study using a target metabolomics approach (VSports)
Abstract
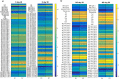
Septic shock remains a major problem in Intensive Care Unit, with high lethality and high-risk second lines treatments. In this preliminary retrospective investigation we examined plasma metabolome and clinical features in a subset of 20 patients with severe septic shock (SOFA score >8), enrolled in the multicenter Albumin Italian Outcome Sepsis study (ALBIOS, NCT00707122). Our purpose was to evaluate the changes of circulating metabolites in relation to mortality as a pilot study to be extended in a larger cohort. Patients were analyzed according to their 28-days and 90-days mortality. Metabolites were measured using a targeted mass spectrometry-based quantitative metabolomic approach that included acylcarnitines, aminoacids, biogenic amines, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, and sugars. Data-mining techniques were applied to evaluate the association of metabolites with mortality. Low unsaturated long-chain phosphatidylcholines and lysophosphatidylcholines species were associated with long-term survival (90-days) together with circulating kynurenine. Moreover, a decrease of these glycerophospholipids was associated to the event at 28-days and 90-days in combination with clinical variables such as cardiovascular SOFA score (28-day mortality model) or renal replacement therapy (90-day mortality model). Early changes in the plasma levels of both lipid species and kynurenine associated with mortality have potential implications for early intervention and discovering new target therapy VSports手机版. .
Figures



V体育2025版 - References
-
- Russell J. A. Management of sepsis. N Engl J Med 355, 1699–713, (2006). - PubMed
-
- Angus D. C. & van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 369, 840–51, (2013). - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. et al. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis 15, 581–614, (2015). - PubMed
-
- Caironi P. et al. Albumin replacement in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. N Engl J Med 370, 1412–21, (2014). - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
-
- Perner A. et al. Hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.42 versus Ringer’s acetate in severe sepsis. N Engl J Med 367, 124–34, (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports app下载 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
"V体育2025版" Substances
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
V体育ios版 - Associated data
"V体育官网" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical (V体育官网入口)

