Xanthine Oxidoreductase-Derived Reactive Species: Physiological and Pathological Effects (VSports在线直播)
- PMID: 26823950
- PMCID: PMC4707389
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3527579
Xanthine Oxidoreductase-Derived Reactive Species: Physiological and Pathological Effects
Abstract
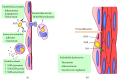
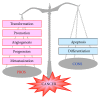
Xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR) is the enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and xanthine to uric acid and is widely distributed among species. In addition to this housekeeping function, mammalian XOR is a physiological source of superoxide ion, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide, which can function as second messengers in the activation of various pathways. This review intends to address the physiological and pathological roles of XOR-derived oxidant molecules VSports手机版. The cytocidal action of XOR products has been claimed in relation to tissue damage, in particular damage induced by hypoxia and ischemia. Attempts to exploit this activity to eliminate unwanted cells via the construction of conjugates have also been reported. Moreover, different aspects of XOR activity related to phlogosis, endothelial activation, leukocyte activation, and vascular tone regulation, have been taken into consideration. Finally, the positive and negative outcomes concerning cancer pathology have been analyzed because XOR products may induce mutagenesis, cell proliferation, and tumor progression, but they are also associated with apoptosis and cell differentiation. In conclusion, XOR activity generates free radicals and other oxidant reactive species that may result in either harmful or beneficial outcomes. .
Figures

"V体育2025版" References
-
- Parks D. A., Granger D. N. Xanthine oxidase: biochemistry, distribution and physiology. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 1986;126(548):87–99. - PubMed
-
- Hille R., Nishino T. Xanthine oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase. The FASEB Journal. 1995;9(11):995–1003. - PubMed
-
- Ames B. N., Cathcart R., Schwiers E., Hochstein P. Uric acid provides an antioxidant defense in humans against oxidant- and radical-caused aging and cancer: a hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1981;78(11):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6858. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
VSports app下载 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
V体育官网入口 - Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
VSports app下载 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

