V体育官网 - MLN4924, a Novel NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, exhibits antitumor activity and enhances cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human cervical carcinoma: in vitro and in vivo study
- PMID: 26807316
- PMCID: PMC4697682
MLN4924, a Novel NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, exhibits antitumor activity and enhances cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human cervical carcinoma: in vitro and in vivo study
"VSports" Abstract
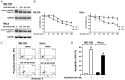
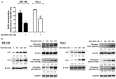
MLN4924, an inhibitor of NEDD8 activating enzyme (NAE), has been reported to have activity against various malignancies. Here, we investigated the antitumor properties of MLN4924 and MLN4924 in combination with cisplatin on human cervical carcinoma (CC) in vitro and in vivo. Two human CC cell lines, ME-180 and HeLa, were used in this study. The cytotoxic effects of MLN4924 and/or cisplatin were measured by cell viability (MTT), proliferation (BrdU incorporation), apoptosis (flow cytometry with annexin V-FITC labeling), and the expression of cell apoptosis-related proteins (Western blotting). In vivo efficacy was determined in Nu/Nu nude mice with ME-180 and HeLa xenografts. The results showed that MLN4924 elicited viability inhibition, anti-proliferation and apoptosis in human CC cells, accompanied by activations of apoptosis-related molecules and Bid, Bcl-2 phosphorylation interruption, and interference with cell cycle regulators VSports手机版. Moreover, MLN4924 caused an endoplasmic reticulum stress response (caspase-4, ATF-4 and CHOP activations) and expression of other cellular stress molecules (JNK and c-Jun activations). Additionally, MLN4924 suppressed growth of CC xenografts in nude mice. Furthermore, we demonstrated that MLN4924 potentiated cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in CC cells with activation of caspases. Consistently with this, MLN4924 significantly enhanced cisplatin-induced growth inhibition of CC xenografts. Together, these findings suggest that MLN4924 alone or in combination with cisplatin is of value in treating human CCs. .
Keywords: MLN4924; apoptosis; cervical carcinoma; neddylation. V体育安卓版.
V体育2025版 - Figures





References
-
- Arbyn M, Castellsagué X, de Sanjosé S, Bruni L, Saraiya M, Bray F, Ferlay J. Worldwide burden of cervical cancer in 2008. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:2675–2686. - PubMed
-
- Blank JL, Liu XJ, Cosmopoulos K, Bouck DC, Garcia K, Bernard H, Tayber O, Hather G, Liu R, Narayanan U, Milhollen MA, Lightcap ES. Novel DNA damage checkpoints mediating cell death induced by the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924. Cancer Res. 2013;73:225–234. - "V体育2025版" PubMed
-
- Bosch FX, Lorincz A, Muñoz N, Meijer CJ, Shah KV. The causal relation between human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2002;55:244–265. - V体育平台登录 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brownell JE, Sintchak MD, Gavin JM, Liao H, Bruzzese FJ, Bump NJ, Soucy TA, Milhollen MA, Yang X, Burkhardt AL, Ma J, Loke HK, Lingaraj T, Wu D, Hamman KB, Spelman JJ, Cullis CA, Langston SP, Vyskocil S, Sells TB, Mallender WD, Visiers I, Li P, Claiborne CF, Rolfe M, Bolen JB, Dick LR. Substrate-assisted inhibition of ubiquitin-like protein-activating enzymes: the NEDD8 E1 inhibitor MLN4924 forms a NEDD8-AMP mimetic in situ. Mol Cell. 2010;37:102–111. - PubMed
VSports - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
