VSports注册入口 - Biological Activities of Uric Acid in Infection Due to Enteropathogenic and Shiga-Toxigenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 26787720
- PMCID: PMC4807499
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01389-15 (V体育安卓版)
Biological Activities of Uric Acid in Infection Due to Enteropathogenic and Shiga-Toxigenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
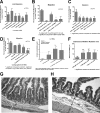
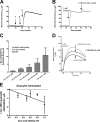
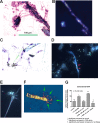
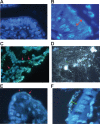
In previous work, we identified xanthine oxidase (XO) as an important enzyme in the interaction between the host and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli(EPEC) and Shiga-toxigenic E. coli(STEC). Many of the biological effects of XO were due to the hydrogen peroxide produced by the enzyme. We wondered, however, if uric acid generated by XO also had biological effects in the gastrointestinal tract. Uric acid triggered inflammatory responses in the gut, including increased submucosal edema and release of extracellular DNA from host cells. While uric acid alone was unable to trigger a chloride secretory response in intestinal monolayers, it did potentiate the secretory response to cyclic AMP agonists. Uric acid crystals were formed in vivo in the lumen of the gut in response to EPEC and STEC infections VSports手机版. While trying to visualize uric acid crystals formed during EPEC and STEC infections, we noticed that uric acid crystals became enmeshed in the neutrophilic extracellular traps (NETs) produced from host cells in response to bacteria in cultured cell systems and in the intestine in vivo Uric acid levels in the gut lumen increased in response to exogenous DNA, and these increases were enhanced by the actions of DNase I. Interestingly, addition of DNase I reduced the numbers of EPEC bacteria recovered after a 20-h infection and protected against EPEC-induced histologic damage. .
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology V体育安卓版. All Rights Reserved. .
Figures

References (VSports注册入口)
-
- Yamada Y, Saito H, Tomioka H, Jidoi J. 1987. Susceptibility of micro-organisms to active oxygen species: sensitivity to the xanthine-oxidase-mediated antimicrobial system. J Gen Microbiol 133:2007–2014. - PubMed
-
- Behrens MD, Wagner WM, Krco CJ, Erskine CL, Kalli KR, Krempski J, Gad EA, Disis ML, Knutson KL. 2008. The endogenous danger signal, crystalline uric acid, signals for enhanced antibody immunity. Blood 111:1472–1479. - PMC (VSports手机版) - PubMed
-
- Martinon F, Petrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J. 2006. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 440:237–241. doi:10.1038/nature04516. - DOI (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育2025版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
Substances
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
VSports注册入口 - Grants and funding
"V体育官网" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
V体育ios版 - Other Literature Sources
Medical (VSports)

