"V体育2025版" Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 26746985
- PMCID: PMC4761283
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.12.014
Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia
Abstract
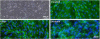
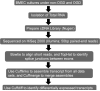
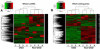
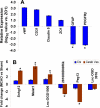
The brain endothelium is an important therapeutic target for the inhibition of cerebrovascular dysfunction in ischemic stroke. Previously, we documented the important regulatory roles of microRNAs in the cerebral vasculature, in particular the cerebral vascular endothelium. However, the functional significance and molecular mechanisms of other classes of non-coding RNAs in the regulation of cerebrovascular endothelial pathophysiology after stroke are completely unknown. Using RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) technology, we profiled long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) expressional signatures in primary brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) after oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD), an in vitro mimic of ischemic stroke conditions. After 16h of OGD exposure, the expression levels for 362 of the 10,677 lncRNAs analyzed changed significantly, including a total of 147 lncRNAs increased and 70 lncRNAs decreased by more than 2-fold. Among them, the most highly upregulated lncRNAs include Snhg12, Malat1, and lnc-OGD 1006, whereas the most highly downregulated lncRNAs include 281008D09Rik, Peg13, and lnc-OGD 3916. Alteration of the most highly upregulated/downregulated ODG-responsive lncRNAs was further confirmed in cultured BMECs after OGD as well as isolated cerebral microvessels in mice following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and 24h reperfusion by the quantitative real-time PCR approach. Moreover, promoter analysis of altered ODG-responsive endothelial lncRNA genes by bioinformatics showed substantial transcription factor binding sites on lncRNAs, implying potential transcriptional regulation of those lncRNAs. These findings are the first to identify OGD-responsive brain endothelial lncRNAs, which suggest potential pathological roles for these lncRNAs in mediating endothelial responses to ischemic stimuli. Endothelial-selective lncRNAs may function as a class of novel master regulators in cerebrovascular endothelial pathologies after ischemic stroke VSports手机版. .
Keywords: Brain microvascular endothelial cells; Ischemic stroke; Long non-coding RNAs; Oxygen–glucose deprivation; RNA sequencing; Transcriptome V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc V体育ios版. All rights reserved. .
Figures
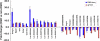
References
-
- Barone FC. Ischemic stroke intervention requires mixed cellular protection of the penumbra. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;10:220–223. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
-
- del Zoppo GJ. Stroke and neurovascular protection. The New England journal of medicine. 2006;354:553–555. - VSports app下载 - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports)
Grants and funding
- "VSports手机版" R01 HL068878/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS086820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS066652/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117491/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL129778/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- "V体育ios版" NS091175/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS094930/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS086820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS094930/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- VSports在线直播 - R01 NS091175/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports注册入口" R01 NS066652/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育平台登录" Other Literature Sources

