"VSports最新版本" Integrative omics reveals MYCN as a global suppressor of cellular signalling and enables network-based therapeutic target discovery in neuroblastoma
- PMID: 26673823
- PMCID: "V体育2025版" PMC4791225
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6568
"VSports在线直播" Integrative omics reveals MYCN as a global suppressor of cellular signalling and enables network-based therapeutic target discovery in neuroblastoma
Abstract
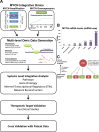
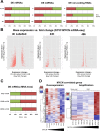
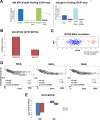
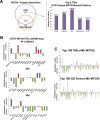
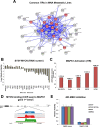
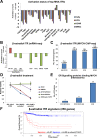
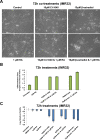
Despite intensive study, many mysteries remain about the MYCN oncogene's functions. Here we focus on MYCN's role in neuroblastoma, the most common extracranial childhood cancer. MYCN gene amplification occurs in 20% of cases, but other recurrent somatic mutations are rare. This scarcity of tractable targets has hampered efforts to develop new therapeutic options. We employed a multi-level omics approach to examine MYCN functioning and identify novel therapeutic targets for this largely un-druggable oncogene. We used systems medicine based computational network reconstruction and analysis to integrate a range of omic techniques: sequencing-based transcriptomics, genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation, siRNA screening and interaction proteomics, revealing that MYCN controls highly connected networks, with MYCN primarily supressing the activity of network components. MYCN's oncogenic functions are likely independent of its classical heterodimerisation partner, MAX. In particular, MYCN controls its own protein interaction network by transcriptionally regulating its binding partners. Our network-based approach identified vulnerable therapeutically targetable nodes that function as critical regulators or effectors of MYCN in neuroblastoma. These were validated by siRNA knockdown screens, functional studies and patient data. We identified β-estradiol and MAPK/ERK as having functional cross-talk with MYCN and being novel targetable vulnerabilities of MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. These results reveal surprising differences between the functioning of endogenous, overexpressed and amplified MYCN, and rationalise how different MYCN dosages can orchestrate cell fate decisions and cancerous outcomes VSports手机版. Importantly, this work describes a systems-level approach to systematically uncovering network based vulnerabilities and therapeutic targets for multifactorial diseases by integrating disparate omic data types. .
Keywords: 4sU-seq; MYC (c-MYC); mRNA sequencing (mRNA-seq); neuroblastoma; transcriptional regulation. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schwab M, Alitalo K, Klempnauer KH, Varmus HE, Bishop JM, Gilbert F, Brodeur G, Goldstein M, Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumor. Nature. 1983;305:245–248. - PubMed
-
- Hatton BA, Knoepfler PS, Kenney AM, Rowitch DH, de Alborán IM, Olson JM, Eisenman RN. N-myc Is an Essential Downstream Effector of Shh Signaling during both Normal and Neoplastic Cerebellar Growth. Cancer Research. 2006;66:8655–8661. - PubMed
-
- Cohn SL, Pearson ADJ, London WB, Monclair T, Ambros PF, Brodeur GM, Faldum A, Hero B, Iehara T, Machin D, Mosseri V, Simon T, Garaventa A, Castel V, Matthay KK. The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) Classification System: An INRG Task Force Report. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2009;27:289–297. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
"V体育安卓版" LinkOut - more resources
"V体育安卓版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports在线直播)
Medical (VSports在线直播)
"VSports" Miscellaneous

