Zn/Cu Levels in the Field of Autism Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 26664435
- PMCID: PMC4670971
Zn/Cu Levels in the Field of Autism Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
"V体育平台登录" Abstract
Objective: There is probably a relationship between zinc/cupper concentration in individuals with autism VSports手机版. The present review was written to estimate this probability by using meta-analysis method. .
Martials & methods: In this meta-analysis of Fixed Effect Model, by searching PubMed, Scopus and Google scholar databases, 11 articles were selected and verified published in 1978 to 2012. I² statistics were calculated to examine heterogeneity V体育安卓版. The information was analyzed by R and STATA Ver. 11. 2. .
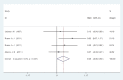
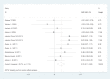
Results: Due to non-uniform measurement methods of Zn/Cu concentrations, the concentration of these elements was measured in various subgroups (plasma, hair and general) in both study cases and controls V体育ios版. There was a significant statistical difference between plasma OR=0. 252 (95% CI: -0. 001-0. 504) and hair OR=0. 27(95% CI: 0. 059-0. 481, P=0. 01) concentrations of Zn/Cu statuses between controls and autistic patients. Using a Fixed Effects Model, the overall integration of data from the two groups was significant as risk factor OR=0. 31(95% CI:0. 16-0. 46, P=0. 001). .
Conclusion: Significant correlation existed between Zn/Cu levels and the development of autistic disorders in general analysis. Therefore, Zn/Cu levels could be mentioned as a pathogenesis reason of autism spectrum disorders. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorders; Concentration; Cupper; Metaanalysis; Zinc V体育平台登录. .
"VSports app下载" Figures




References
-
- Arnold LE, Farmer C, Kraemer HC et al. Moderators, Mediators, and Other Predictors of Risperidone Response in Children with Autistic Disorder and Irritability. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2010;20(2):83–92. - PMC (V体育官网入口) - PubMed
-
- Karimzadeh P. Recent finding about etiology of autism. Rehabilitation. 2000;1(2):58–63.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000. ISBN 0-89042-025-4. OCLC 768475353.
-
- Abrahams BS, Geschwind DH. Advances in autism genetics: on the threshold of a new neurobiology. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9(5):341–55. - "V体育ios版" PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
