Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells
- PMID: 26649828
- PMCID: PMC4700594
- DOI: 10.1038/nature16140
Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells
"V体育ios版" Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells.Nature. 2019 Jul;571(7763):E2. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1328-7. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31227820
Abstract
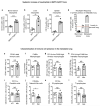
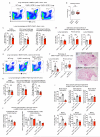
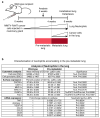
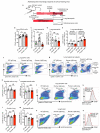
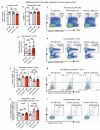
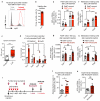
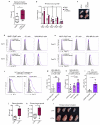
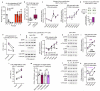
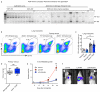
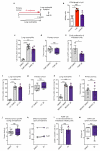
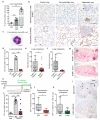
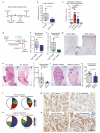
Despite progress in the development of drugs that efficiently target cancer cells, treatments for metastatic tumours are often ineffective. The now well-established dependency of cancer cells on their microenvironment suggests that targeting the non-cancer-cell component of the tumour might form a basis for the development of novel therapeutic approaches. However, the as-yet poorly characterized contribution of host responses during tumour growth and metastatic progression represents a limitation to exploiting this approach. Here we identify neutrophils as the main component and driver of metastatic establishment within the (pre-)metastatic lung microenvironment in mouse breast cancer models. Neutrophils have a fundamental role in inflammatory responses and their contribution to tumorigenesis is still controversial. Using various strategies to block neutrophil recruitment to the pre-metastatic site, we demonstrate that neutrophils specifically support metastatic initiation. Importantly, we find that neutrophil-derived leukotrienes aid the colonization of distant tissues by selectively expanding the sub-pool of cancer cells that retain high tumorigenic potential. Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of the leukotriene-generating enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase (Alox5) abrogates neutrophil pro-metastatic activity and consequently reduces metastasis. Our results reveal the efficacy of using targeted therapy against a specific tumour microenvironment component and indicate that neutrophil Alox5 inhibition may limit metastatic progression. VSports手机版.
Figures


Comment in
-
Arresting supporters: targeting neutrophils in metastasis.Cell Res. 2016 Mar;26(3):273-4. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.17. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 26823207 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour immunology: Neutrophils help tumours spread.Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 Feb;16(2):74-5. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.17. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26831524 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bald T, et al. Ultraviolet-radiation-induced inflammation promotes angiotropism and metastasis in melanoma. Nature. 2014;507:109–113. - PubMed
-
- Galdiero MR, et al. Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in cancer. Immunobiology. 2013;218:1402–1410. - PubMed
-
- Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Aburatani H, Maru Y. Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nature cell biology. 2006;8:1369–1375. - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
VSports手机版 - Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

