Reversal of Acute Kidney Injury-Induced Neutrophil Dysfunction: A Critical Role for Resistin
- PMID: 26646460
- PMCID: PMC4896858
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001472
Reversal of Acute Kidney Injury-Induced Neutrophil Dysfunction: A Critical Role for Resistin
VSports最新版本 - Abstract
Objectives: To assess the reversibility of acute kidney injury-induced neutrophil dysfunction and to identify involved mechanisms. VSports手机版.
Design: Controlled laboratory experiment and prospective observational clinical study V体育安卓版. .
Setting: University laboratory and hospital. V体育ios版.
Subjects: C57BL/6 wild-type mice VSports最新版本. .
Patients: Patients with septic shock with or without acute kidney injury V体育平台登录. .
Interventions: Murine acute kidney injury was induced by intraperitoneal injections of folic acid (nephrotoxic acute kidney injury) or by IM injections of glycerol (rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury). After 24 hours, we incubated isolated neutrophils for 3 hours in normal mouse serum or minimum essential medium buffer. We further studied the effects of plasma samples from 13 patients with septic shock (with or without severe acute kidney injury) on neutrophilic-differentiated NB4 cells VSports注册入口. .
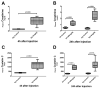
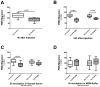
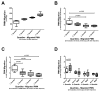
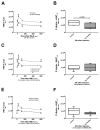
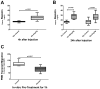
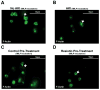
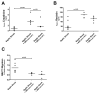
Measurements and main results: Experimental acute kidney injury significantly inhibited neutrophil migration and intracellular actin polymerization V体育官网入口. Plasma levels of resistin, a proinflammatory cytokine and uremic toxin, were significantly elevated during both forms of acute kidney injury. Incubation in serum or minimum essential medium buffer restored normal neutrophil function. Resistin by itself was able to induce acute kidney injury-like neutrophil dysfunction in vitro. Plasma resistin was significantly higher in patients with septic shock with acute kidney injury compared with patients with septic shock alone. Compared with plasma from patients with septic shock, plasma from patients with septic shock and acute kidney injury inhibited neutrophilic-differentiated NB4 cell migration. Even after 4 days of renal replacement therapy, plasma from patients with septic shock plus acute kidney injury still showed elevated resistin levels and inhibited neutrophilic-differentiated NB4 cell migration. Resistin inhibited neutrophilic-differentiated NB4 cell migration and intracellular actin polymerization at concentrations seen during acute kidney injury, but not at normal physiologic concentrations. .
Conclusions: Acute kidney injury-induced neutrophil dysfunction is reversible in vitro VSports在线直播. However, standard renal replacement therapy does not correct this defect in patients with septic shock and acute kidney injury. Resistin is greatly elevated during acute kidney injury, even with ongoing renal replacement therapy, and is sufficient to cause acute kidney injury-like neutrophil dysfunction by itself. .
Figures

Comment in (VSports app下载)
-
Resistin Resets Neutrophil Function in Kidney Diseases.Crit Care Med. 2016 Jul;44(7):1454-5. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001538. Crit Care Med. 2016. PMID: 27309176 No abstract available.
V体育安卓版 - References
-
- Hoste E, Schurgers M. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury: How big is the problem? Crit Care Med. 2008;36(4 Suppl):S146–151. - PubMed (VSports最新版本)
-
- Singbartl K, Kellum J. AKI in the ICU: definition, epidemiology, risk stratification, and outcomes. Kidney Int. 2012;81(9):819–825. - PubMed (V体育平台登录)
-
- Metnitz P, Krenn C, Steltzer H, et al. Effect of acute renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy on outcome in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2002;30(9):2051–2058. - PubMed (V体育2025版)
-
- Ishani A, Xue J, Himmelfarb J, et al. Acute kidney injury increases risk of ESRD among elderly. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(1):223–228. - V体育官网入口 - PMC - PubMed
"V体育ios版" Publication types
MeSH terms (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
"V体育平台登录" Grants and funding
"VSports最新版本" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育平台登录)
Medical

