ATP-binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 5 (ABCC5) Functions as an Efflux Transporter of Glutamate Conjugates and Analogs (V体育官网入口)
- PMID: 26515061
- PMCID: PMC4683265
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.692103
ATP-binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 5 (ABCC5) Functions as an Efflux Transporter of Glutamate Conjugates and Analogs
Abstract (VSports app下载)
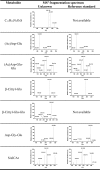
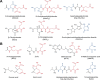
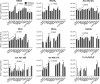
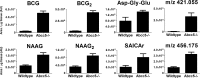
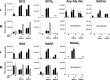
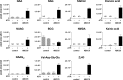
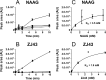
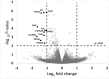
The ubiquitous efflux transporter ABCC5 (ATP-binding cassette subfamily C member 5) is present at high levels in the blood-brain barrier, neurons, and glia, but its in vivo substrates and function are not known. Using untargeted metabolomic screens, we show that Abcc5(-/-) mice accumulate endogenous glutamate conjugates in several tissues, but brain in particular VSports手机版. The abundant neurotransmitter N-acetylaspartylglutamate was 2. 4-fold higher in Abcc5(-/-) brain. The metabolites that accumulated in Abcc5(-/-) tissues were depleted in cultured cells that overexpressed human ABCC5. In a vesicular membrane transport assay, ABCC5 also transported exogenous glutamate analogs, like the classic excitotoxic neurotoxins kainic acid, domoic acid, and NMDA; the therapeutic glutamate analog ZJ43; and, as previously shown, the anti-cancer drug methotrexate. Glutamate conjugates and analogs are of physiological relevance because they can affect the function of glutamate, the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. After CO2 asphyxiation, several immediate early genes were expressed at lower levels in Abcc5(-/-) brains than in wild type brains, suggesting altered glutamate signaling. Our results show that ABCC5 is a general glutamate conjugate and analog transporter that affects the disposition of endogenous metabolites, toxins, and drugs. .
Keywords: MRP5; blood-brain barrier; brain; drug transport; glutamate; neurotoxin; neurotransmitter transport. V体育安卓版.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc V体育ios版. .
"V体育官网" Figures

References
-
- Borst P., de Wolf C., and van de Wetering K. (2007) Multidrug resistance-associated proteins 3, 4, and 5. Pflügers Arch. 453, 661–673 - PubMed
-
- Dean M., and Allikmets R. (2001) Complete characterization of the human ABC gene family. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 33, 475–479 - PubMed
-
- Belinsky M. G., Bain L. J., Balsara B. B., Testa J. R., and Kruh G. D. (1998) Characterization of MOAT-C and MOAT-D, new members of the MRP/cMOAT subfamily of transporter proteins. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 90, 1735–1741 - PubMed
-
- Kool M., de Haas M., Scheffer G. L., Scheper R. J., van Eijk M. J., Juijn J. A., Baas F., and Borst P. (1997) Analysis of expression of cMOAT (MRP2), MRP3, MRP4, and MRP5, homologues of the multidrug resistance-associated protein gene (MRP1), in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 57, 3537–3547 - PubMed
-
- McAleer M. A., Breen M. A., White N. L., and Matthews N. (1999) pABC11 (also known as MOAT-C and MRP5), a member of the ABC family of proteins, has anion transporter activity but does not confer multidrug resistance when overexpressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23541–23548 - PubMed
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Associated data
"VSports app下载" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

