Antibiotics in neonatal life increase murine susceptibility to experimental psoriasis
- PMID: 26416167
- PMCID: PMC4598725
- DOI: VSports - 10.1038/ncomms9424
Antibiotics in neonatal life increase murine susceptibility to experimental psoriasis
Abstract
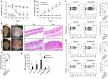
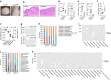
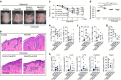
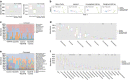
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disease affecting ∼2% of the world's population, but the aetiology remains incompletely understood. Recently, microbiota have been shown to differentially regulate the development of autoimmune diseases, but their influence on psoriasis is incompletely understood. We show here that adult mice treated with antibiotics that target Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria develop ameliorated psoriasiform dermatitis induced by imiquimod, with decreased pro-inflammatory IL-17- and IL-22-producing T cells. Surprisingly, mice treated neonatally with these antibiotics develop exacerbated psoriasis induced by imiquimod or recombinant IL-23 injection when challenged as adults, with increased IL-22-producing γδ(+) T cells. 16S rRNA gene compositional analysis reveals that neonatal antibiotic-treatment dysregulates gut and skin microbiota in adults, which is associated with increased susceptibility to experimental psoriasis. This link between neonatal antibiotic-mediated imbalance in microbiota and development of experimental psoriasis provides precedence for further investigation of its specific aetiology as it relates to human psoriasis VSports手机版. .
Figures
References
-
- Nestle F. O., Kaplan D. H. & Barker J. Psoriasis. New Engl. J. Med 361, 496–509 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Parisi R. et al.. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J. Invest. Dermatol. 133, 377–385 (2013). - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
-
- Perera G. K., Di Meglio P. & Nestle F. O. Psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 7, 385–422 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Wu H. J. et al.. Gut-residing segmented filamentous bacteria drive autoimmune arthritis via T helper 17 cells. Immunity 32, 815–827 (2010). - VSports最新版本 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types (VSports app下载)
MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
VSports最新版本 - Substances
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

