Histone deacetylase inhibition activates Nrf2 and protects against osteoarthritis
- PMID: 26408027
- PMCID: PMC4583998
- DOI: VSports最新版本 - 10.1186/s13075-015-0774-3
Histone deacetylase inhibition activates Nrf2 and protects against osteoarthritis
VSports - Abstract
Introduction: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common joint disease that can cause gradual disability among the aging population. Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) is a key transcription factor that regulates the expression of phase II antioxidant enzymes that provide protection against oxidative stress and tissue damage VSports手机版. The use of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy for various diseases. They have displayed chondroprotective effects in various animal models of arthritis. Previous studies have established that Nrf2 acetylation enhances Nrf2 functions. Here we explore the role of Nrf2 in the development of OA and the involvement of Nrf2 acetylation in HDACi protection of OA. .
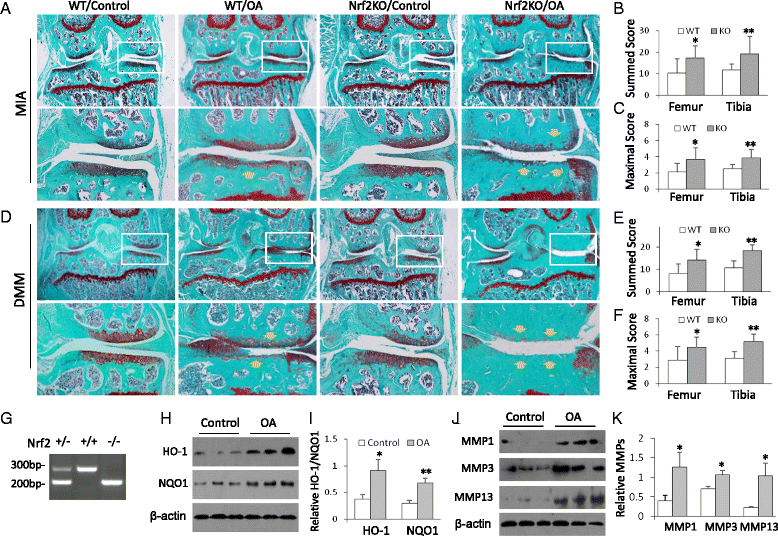
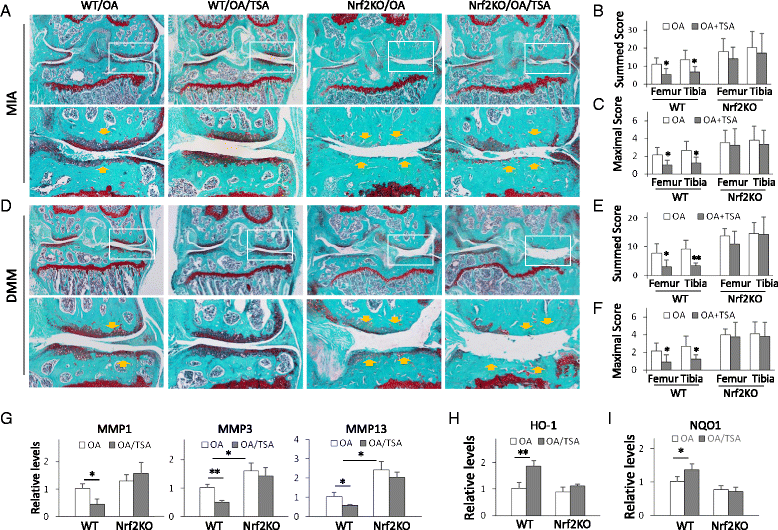
Methods: Two OA models-monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) articular injection and destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM)-were used with wild-type (WT) and Nrf2-knockout (Nrf2-KO) mice to demonstrate the role of Nrf2 in OA progression. A pan-HDACi, trichostatin A (TSA), was administered to examine the effectiveness of HDACi on protection from cartilage damage. The histological sections were scored. The expression of OA-associated matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) 1, 3, and 13 and proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 were assayed. The effectiveness of HDACi on OA protection was compared between WT and Nrf2-KO mice. V体育安卓版.
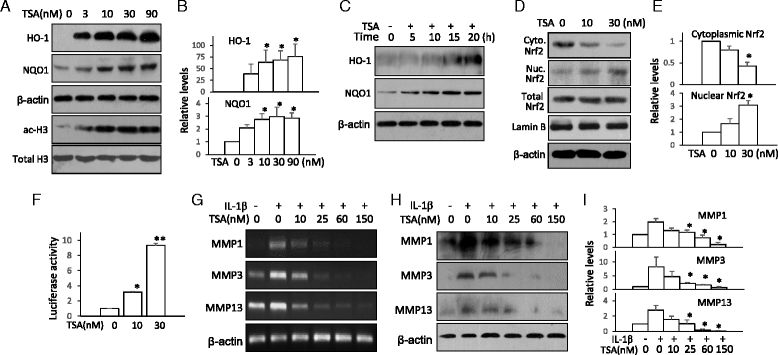
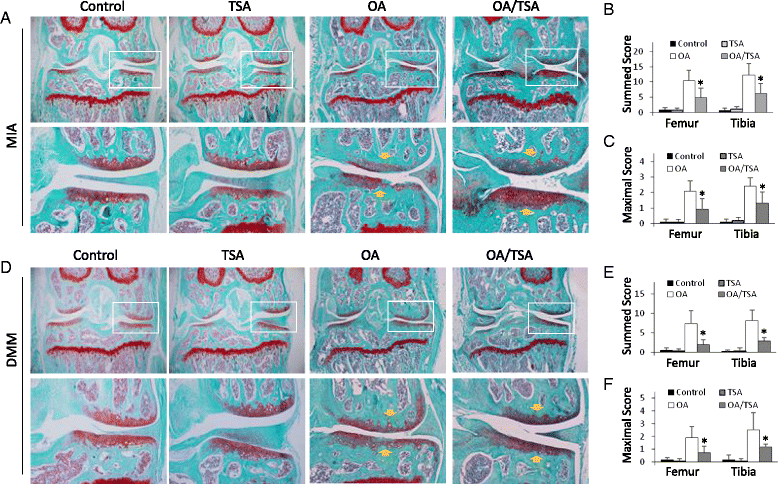
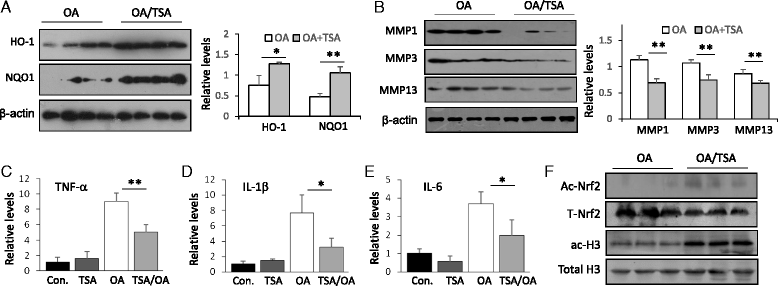
Results: Nrf2-KO mice displayed more severe cartilage damage in both the MIA and DMM models. TSA promoted the induction of Nrf2 downstream proteins in SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells and in mouse joint tissues. TSA also reduced the expression of OA-associated proteins MMP1, MMP3, and MMP13 and proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. TSA markedly reduced the cartilage damage in both OA models but offered no significant protection in Nrf2-KO mice. V体育ios版.
Conclusions: Nrf2 has a major chondroprotective role in progression of OA and is a critical molecule in HDACi-mediated OA protection VSports最新版本. .
Figures
References
-
- Su SC, Tanimoto K, Tanne Y, Kunimatsu R, Hirose N, Mitsuyoshi T, et al. Celecoxib exerts protective effects on extracellular matrix metabolism of mandibular condylar chondrocytes under excessive mechanical stress. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22:845–51. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2014.03.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao J, Zhang B, Li S, Zeng L, Chen Y, Fang J. Mangiferin increases Nrf2 protein stability by inhibiting its ubiquitination and degradation in human HL60 myeloid leukemia cells. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33:1348–54. - PubMed
"V体育平台登录" Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育安卓版" Other Literature Sources
"VSports注册入口" Medical
VSports app下载 - Research Materials
Miscellaneous

