Cabozantinib versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 26406150
- PMCID: PMC5024539
- DOI: VSports在线直播 - 10.1056/NEJMoa1510016
Cabozantinib versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Cabozantinib is an oral, small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) as well as MET and AXL, each of which has been implicated in the pathobiology of metastatic renal-cell carcinoma or in the development of resistance to antiangiogenic drugs. This randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial evaluated the efficacy of cabozantinib, as compared with everolimus, in patients with renal-cell carcinoma that had progressed after VEGFR-targeted therapy. VSports手机版.
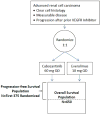
Methods: We randomly assigned 658 patients to receive cabozantinib at a dose of 60 mg daily or everolimus at a dose of 10 mg daily. The primary end point was progression-free survival. Secondary efficacy end points were overall survival and objective response rate V体育安卓版. .
Results: Median progression-free survival was 7. 4 months with cabozantinib and 3. 8 months with everolimus. The rate of progression or death was 42% lower with cabozantinib than with everolimus (hazard ratio, 0. 58; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0. 45 to 0. 75; P<0. 001). The objective response rate was 21% with cabozantinib and 5% with everolimus (P<0. 001). A planned interim analysis showed that overall survival was longer with cabozantinib than with everolimus (hazard ratio for death, 0. 67; 95% CI, 0. 51 to 0. 89; P=0. 005) but did not cross the significance boundary for the interim analysis. Adverse events were managed with dose reductions; doses were reduced in 60% of the patients who received cabozantinib and in 25% of those who received everolimus. Discontinuation of study treatment owing to adverse events occurred in 9% of the patients who received cabozantinib and in 10% of those who received everolimus. V体育ios版.
Conclusions: Progression-free survival was longer with cabozantinib than with everolimus among patients with renal-cell carcinoma that had progressed after VEGFR-targeted therapy. (Funded by Exelixis; METEOR ClinicalTrials. gov number, NCT01865747 VSports最新版本. ). .
Figures (VSports注册入口)
Comment in
-
Renal-Cell Cancer--Targeting an Immune Checkpoint or Multiple Kinases.N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 5;373(19):1872-4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1511252. Epub 2015 Sep 25. N Engl J Med. 2015. PMID: 26406149 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
V体育平台登录 - CheckMate for advanced-stage ccRCC? Nivolumab and cabozantinib aMETEORate poor survival.Nat Rev Urol. 2015 Dec;12(12):651. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2015.246. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Nat Rev Urol. 2015. PMID: 26458750 No abstract available.
-
Kidney cancer: CheckMate for advanced-stage ccRCC? Nivolumab and cabozantinib aMETEORate poor survival.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015 Nov;12(11):621. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.178. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26462125 No abstract available.
-
Words of Wisdom. Re: Nivolumab Versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. (VSports app下载)Eur Urol. 2016 Apr;69(4):753-4. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.01.018. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 26972496 No abstract available.
V体育官网 - References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN. Kidney Cancer estimated incidence and mortality, all ages, both sexes. 2012 http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_population.aspx. Accessed April 2015.
-
- Gupta K, Miller JD, Li JZ, Russell MW, Charbonneau C. Epidemiologic and socioeconomic burden of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC): a literature review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2008;34:193–205. - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
-
- Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin North Am. 2003;30:843–52. - PubMed
-
- Kroeger N, Choueiri TK, Lee JL, et al. Survival outcome and treatment response of patients with late relapse from renal cell carcinoma in the era of targeted therapy. Eur Urol. 2014;65:1086–92. - PubMed
-
- Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC, et al. Prediction of progression after radical nephrectomy for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a stratification tool for prospective clinical trials. Cancer. 2003;97:1663–71. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Associated data
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials (VSports app下载)
"VSports app下载" Miscellaneous