V体育ios版 - Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 26403645
- PMCID: PMC4688087
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.28251 (V体育官网)
"VSports注册入口" Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract (V体育官网)
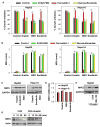
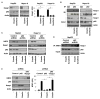
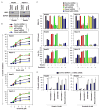
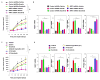
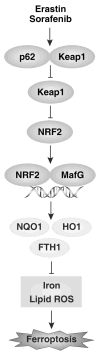
Ferroptosis is a recently recognized form of regulated cell death caused by an iron-dependent accumulation of lipid reactive oxygen species. However, the molecular mechanisms regulating ferroptosis remain obscure. Here, we report that nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) plays a central role in protecting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells against ferroptosis. Upon exposure to ferroptosis-inducing compounds (e VSports手机版. g. , erastin, sorafenib, and buthionine sulfoximine), p62 expression prevented NRF2 degradation and enhanced subsequent NRF2 nuclear accumulation through inactivation of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1. Additionally, nuclear NRF2 interacted with transcriptional coactivator small v-maf avian musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog proteins such as MafG and then activated transcription of quinone oxidoreductase-1, heme oxygenase-1, and ferritin heavy chain-1. Knockdown of p62, quinone oxidoreductase-1, heme oxygenase-1, and ferritin heavy chain-1 by RNA interference in HCC cells promoted ferroptosis in response to erastin and sorafenib. Furthermore, genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of NRF2 expression/activity in HCC cells increased the anticancer activity of erastin and sorafenib in vitro and in tumor xenograft models. .
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate novel molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of ferroptosis; the status of NRF2 is a key factor that determines the therapeutic response to ferroptosis-targeted therapies in HCC cells V体育安卓版. .
© 2015 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. V体育ios版.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. - PubMed
-
- Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, Amadori D, Santoro A, Figer A, De Greve J, et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4293–4300. - PubMed
"V体育安卓版" Publication types
- "V体育官网" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
Substances
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

