A novel exon in the human Ca2+-activated Cl- channel Ano1 imparts greater sensitivity to intracellular Ca2
- PMID: 26359375
- PMCID: PMC4628966
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00074.2015
A novel exon in the human Ca2+-activated Cl- channel Ano1 imparts greater sensitivity to intracellular Ca2
Abstract
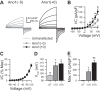
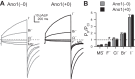
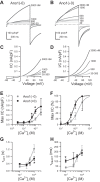
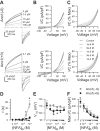
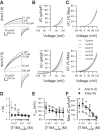
Anoctamin 1 (Ano1; TMEM16A) is a Ca(2+)-activated Cl(-) channel (CACC) expressed in interstitial cells of Cajal. The mechanisms by which Ca(2+) regulates Ano1 are incompletely understood. In the gastrointestinal tract, Ano1 is required for normal slow wave activity and is involved in regulating cell proliferation. Splice variants of Ano1 have varying electrophysiological properties and altered expression in disease states. Recently, we identified a transcript for human Ano1 containing a novel exon-"exon 0" upstream of and in frame with exon 1. The electrophysiological properties of this longer Ano1 isoform are unknown. Our aim was to determine the functional contribution of the newly identified exon to the Ca(2+) sensitivity and electrophysiological properties of Ano1. Constructs with [Ano1(+0)] or without [Ano1(-0)] the newly identified exon were transfected into human embryonic kidney-293 cells. Voltage-clamp electrophysiology was used to determine voltage- and time-dependent parameters of whole cell Cl(-) currents between isoforms with varying concentrations of intracellular Ca(2+), extracellular anions, or Cl(-) channel inhibitors. We found that exon 0 did not change voltage sensitivity and had no impact on the relative permeability of Ano1 to most anions. Ano1(+0) exhibited greater changes in current density but lesser changes in kinetics than Ano1(-0) in response to varying intracellular Ca(2+). The CACC inhibitor niflumic acid inhibited current with greater efficacy and higher potency against Ano1(+0) compared with Ano1(-0) VSports手机版. Likewise, the Ano1 inhibitor T16Ainh-A01 reduced Ano1(+0) more than Ano1(-0). In conclusion, human Ano1 containing exon 0 imparts its Cl(-) current with greater sensitivity to intracellular Ca(2+) and CACC inhibitors. .
Keywords: T16Ainh-A01; TMEM16A; anoctamin 1; electrophysiology; ion channels; niflumic acid V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society. V体育ios版.
Figures
References (VSports)
-
- Bradley E, Fedigan S, Webb T, Hollywood MA, Thornbury KD, McHale NG, Sergeant GP. Pharmacological characterization of TMEM16A currents. Channels 8: 308–320, 2014. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Britschgi A, Bill A, Brinkhaus H, Rothwell C, Clay I, Duss S, Rebhan M, Raman P, Guy CT, Wetzel K, George E, Popa MO, Lilley S, Choudhury H, Gosling M, Wang L, Fitzgerald S, Borawski J, Baffoe J, Labow M, Gaither LA, Bentires-Alj M. Calcium-activated chloride channel ANO1 promotes breast cancer progression by activating EGFR and CAMK signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: E1026–E1034, 2013. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caputo A, Caci E, Ferrera L, Pedemonte N, Barsanti C, Sondo E, Pfeffer U, Ravazzolo R, Zegarra-Moran O, Galietta LJ. TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity. Science 322: 590–594, 2008. - PubMed
V体育平台登录 - Publication types
- Actions (VSports)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Grants and funding (V体育ios版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育平台登录" Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

