Necroinflammation in Kidney Disease
- PMID: 26334031
- PMCID: PMC4696588
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015040405
Necroinflammation in Kidney Disease
V体育2025版 - Abstract
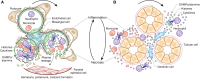
The bidirectional causality between kidney injury and inflammation remains an area of unexpected discoveries. The last decade unraveled the molecular mechanisms of sterile inflammation, which established danger signaling via pattern recognition receptors as a new concept of kidney injury-related inflammation. In contrast, renal cell necrosis remained considered a passive process executed either by the complement-related membrane attack complex, exotoxins, or cytotoxic T cells. Accumulating data now suggest that renal cell necrosis is a genetically determined and regulated process involving specific outside-in signaling pathways VSports手机版. These findings support a unifying theory in which kidney injury and inflammation are reciprocally enhanced in an autoamplification loop, referred to here as necroinflammation. This integrated concept is of potential clinical importance because it offers numerous innovative molecular targets for limiting kidney injury by blocking cell death, inflammation, or both. Here, the contribution of necroinflammation to AKI is discussed in thrombotic microangiopathies, necrotizing and crescentic GN, acute tubular necrosis, and infective pyelonephritis or sepsis. Potential new avenues are further discussed for abrogating necroinflammation-related kidney injury, and questions and strategies are listed for further exploration in this evolving field. .
Keywords: Immunology and pathology; acute renal failure; kidney failure. V体育安卓版.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology V体育ios版. .
VSports在线直播 - Figures

References
-
- Wallach D, Kang TB, Kovalenko A: Concepts of tissue injury and cell death in inflammation: A historical perspective. Nat Rev Immunol 14: 51–59, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Barry M, Bleackley RC: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes: All roads lead to death. Nat Rev Immunol 2: 401–409, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Zipfel PF, Skerka C: Complement regulators and inhibitory proteins. Nat Rev Immunol 9: 729–740, 2009 - "V体育2025版" PubMed
-
- Allam R, Anders HJ: The role of innate immunity in autoimmune tissue injury. Curr Opin Rheumatol 20: 538–544, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
"VSports手机版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (VSports)
Other Literature Sources

