Characterizing unmet medical need and the potential role of new biologic treatment options in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease: a systematic review and clinician surveys
- PMID: 25933126
- PMCID: PMC4892747
- DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000378
"V体育平台登录" Characterizing unmet medical need and the potential role of new biologic treatment options in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease: a systematic review and clinician surveys
VSports手机版 - Abstract
Objectives: Comparative outcomes of patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) prescribed a biologic therapy are inconclusive. The aim of this research was to characterize the degree of unmet medical need in patients with UC or CD and to identify the potential role for new therapies. VSports手机版.
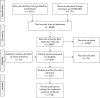
Methods: A systematic literature review was undertaken of studies reporting outcomes associated with the use of existing biologic therapies in patients with UC or CD, focusing on the nature and rate of treatment failure. To complement the systematic review, contemporaneous data were obtained from a survey of practising gastroenterologists in the UK and France. Data were qualitatively combined in a narrative framework to evaluate the degree of unmet medical need among patients with UC or CD V体育安卓版. .
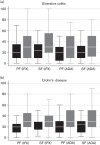
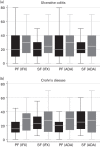
Results: Studies identified in the systematic review (n = 120) were heterogeneous, particularly with respect to the definitions of treatment failure; estimates of treatment failure were high but uncertain. On the basis of standardized definitions, estimates of treatment failure provided by clinicians (n = 102) were high, and they were higher for second-line treatment failure (primary: ≤ 37%; secondary: ≤ 41%) compared with first-line treatment failure (primary: ≤ 26%; secondary: ≤ 28%). The majority of the systematic review and survey data were reflective of outcomes with infliximab and adalimumab. V体育ios版.
Conclusion: High treatment failure rates associated with existing biologics, identified by the review and clinician surveys, indicate a need for other biologic treatment options to improve the management and outcomes for people with UC and CD. Outcomes associated with existing and new biologic treatments should be investigated in head-to-head randomized trials in the context of their likely uses in clinical practice. VSports最新版本.
Figures
"VSports手机版" References
-
- Baumgart DC, Carding SR. Inflammatory bowel disease: cause and immunobiology. Lancet 2007; 369:1627–1640. - PubMed
-
- Pithadia AB, Jain S. Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Pharmacol Rep 2011; 63:629–642. - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
-
- Janssen Biologics BV. Summary of product characteristics. Remicade. 2013. Available at: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info.... [Accessed 9 January 2015].
-
- AbbVie Ltd. Summary of product characteristics. Humira. 2014. Available at: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info.... [Accessed 9 January 2015].
-
- UCB Pharma SA. Summary of product characteristics. Cimzia 2014. Available at: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info.... [Accessed 9 January 2015].
VSports app下载 - Publication types
- Actions (VSports app下载)
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Substances (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (VSports app下载)
Medical

