Immune evasion activities of accessory proteins Vpu, Nef and Vif are conserved in acute and chronic HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 25827531
- PMCID: PMC4503796
- DOI: "VSports最新版本" 10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.015
"V体育ios版" Immune evasion activities of accessory proteins Vpu, Nef and Vif are conserved in acute and chronic HIV-1 infection
Abstract
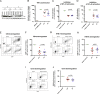
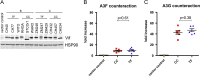
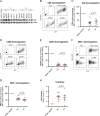
Heterosexual HIV-1 transmission has been identified as a genetic bottleneck and a single transmitted/founder (T/F) variant with reduced sensitivity to type I interferon initiates productive infection in most cases VSports手机版. We hypothesized that particularly active accessory protein(s) may confer T/F viruses with a selective advantage in establishing HIV infection. Thus, we tested vpu, vif and nef alleles from six T/F and six chronic (CC) viruses in assays for 9 immune evasion activities involving the counteraction of interferon-stimulated genes and modulation of ligands known to activate innate immune cells. All functions were highly conserved with no significant differences between T/F and CC viruses, suggesting that these accessory protein functions are important throughout the course of infection. .
Keywords: Accessory; Acute; Chronic; HIV; Nef; Vif; Vpu V体育安卓版. .
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. V体育ios版.
"VSports最新版本" Figures
"VSports app下载" References
-
- Apolonia L., Schulz R., Curk T., Rocha P., Swanson C.M., Schaller T., Ule J., Malim M.H. Promiscuous RNA binding ensures effective encapsidation of APOBEC3 proteins by HIV-1. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1004609. - PMC (V体育安卓版) - PubMed
-
- Baalwa J., Wang S., Parrish N.F., Decker J.M., Keele B.F., Learn G.H., Yue L., Ruzagira E., Ssemwanga D., Kamali A., Amornkul P.N., Price M.A., Kappes J.C., Karita E., Kaleebu P., Sanders E., Gilmour J., Allen S., Hunter E., Montefiori D.C., Haynes B.F., Cormier E., Hahn B.H., Shaw G.M. Molecular identification, cloning and characterization of transmitted/founder HIV-1 subtype A, D and A/D infectious molecular clones. Virology. 2013;436:33–48. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bishop K.N., Holmes R.K., Sheehy A.M., Davidson N.O., Cho S.J., Malim M.H. Cytidine deamination of retroviral DNA by diverse APOBEC proteins. Curr. Biol. CB. 2004;14:1392–1396. - PubMed
-
- Bour S., Perrin C., Akari H., Strebel K. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein inhibits NF-kappa B activation by interfering with beta TrCP-mediated degradation of Ikappa B. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:15920–15928. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
Substances
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports注册入口" Full Text Sources
"VSports最新版本" Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

