The nucleolar ubiquitin-specific protease USP36 deubiquitinates and stabilizes c-Myc
- PMID: 25775507
- PMCID: PMC4378440
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1411713112
The nucleolar ubiquitin-specific protease USP36 deubiquitinates and stabilizes c-Myc
Abstract
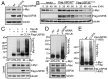
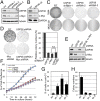
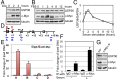
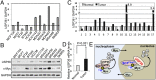
c-Myc protein stability and activity are tightly regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Aberrant stabilization of c-Myc contributes to many human cancers. c-Myc is ubiquitinated by SCF(Fbw7) (a SKP1-cullin-1-F-box complex that contains the F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7, Fbw7, as the F-box protein) and several other ubiquitin ligases, whereas it is deubiquitinated and stabilized by ubiquitin-specific protease (USP) 28. The bulk of c-Myc degradation appears to occur in the nucleolus. However, whether c-Myc is regulated by deubiquitination in the nucleolus is not known. Here, we report that the nucleolar deubiquitinating enzyme USP36 is a novel c-Myc deubiquitinase. USP36 interacts with and deubiquitinates c-Myc in cells and in vitro, leading to the stabilization of c-Myc. This USP36 regulation of c-Myc occurs in the nucleolus. Interestingly, USP36 interacts with the nucleolar Fbw7γ but not the nucleoplasmic Fbw7α. However, it abolished c-Myc degradation mediated both by Fbw7γ and by Fbw7α. Consistently, knockdown of USP36 reduces the levels of c-Myc and suppresses cell proliferation. We further show that USP36 itself is a c-Myc target gene, suggesting that USP36 and c-Myc form a positive feedback regulatory loop. High expression levels of USP36 are found in a subset of human breast and lung cancers. Altogether, these results identified USP36 as a crucial and bono fide deubiquitinating enzyme controlling c-Myc's nucleolar degradation pathway VSports手机版. .
Keywords: USP36; c-Myc; deubiquitination; nucleolus; ubiquitination. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Adhikary S, Eilers M. Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(8):635–645. - PubMed
-
- Meyer N, Penn LZ. Reflecting on 25 years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(12):976–990. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- van Riggelen J, Yetil A, Felsher DW. MYC as a regulator of ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(4):301–309. - PubMed
-
- Nesbit CE, Tersak JM, Prochownik EV. MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene. 1999;18(19):3004–3016. - VSports - PubMed
Publication types (VSports手机版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports手机版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases (VSports app下载)
Research Materials

