Down-regulation of miR-223 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 25638153
- PMCID: PMC4359328 (V体育平台登录)
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2714
"V体育官网" Down-regulation of miR-223 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
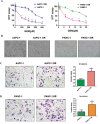
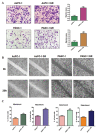
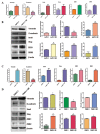
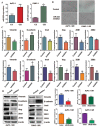
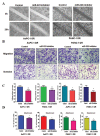
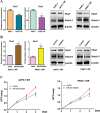
Recent studies have demonstrated that acquisition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is associated with drug resistance in pancreatic cancer cells; however, the underlying mechanisms are not fully elucidated. Emerging evidence suggests that microRNAs play a crucial role in controlling EMT. The aims of this study were to explore the potential role of miR-223 in governing EMT in gemcitabine-resistant (GR) pancreatic cancer cells. To achieve this goal, real-time reverse transcription-PCR and western blot analysis were used to validate whether GR cells acquired EMT in AsPC-1 and PANC-1 cells. Invasion, migration, and detachment assays were performed to further identify the EMT characteristics in GR cells. The miR-223 inhibitor was used to determine its role in GR-induced EMT. We found that GR cells acquired EMT features, which obtained elongated fibroblastoid morphology, decreased expression of epithelial marker E-cadherin, and up-regulation of mesenchymal markers VSports手机版. Furthermore, we observed that GR cells are associated with high expression of miR-223. Notably, inhibition of miR-223 led to the reversal of EMT phenotype. More importantly, miR-223 governs GR-induced EMT in part due to down-regulation of its target Fbw7 and subsequent upregulation of Notch-1 in pancreatic cancer. Our study implied that down-regulation of miR-223 could be a novel therapy for pancreatic cancer. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
VSports最新版本 - References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Paulson AS, Tran Cao HS, Tempero MA, Lowy AM. Therapeutic advances in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1316–1326. - PubMed
-
- Oettle H. Progress in the knowledge and treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer: From benchside to bedside. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014;40:1039–1047. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- de Sousa Cavalcante L, Monteiro G. Gemcitabine: Metabolism and molecular mechanisms of action, sensitivity and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;741C:8–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
VSports最新版本 - Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育ios版)
"VSports app下载" Other Literature Sources
Medical

