Intestinal epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 25593900
- PMCID: PMC4292184
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2014.00024
Intestinal epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease (VSports)
"V体育安卓版" Abstract
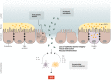
The intestinal epithelium has a strategic position as a protective physical barrier to luminal microbiota and actively contributes to the mucosal immune system. This barrier is mainly formed by a monolayer of specialized intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) that are crucial in maintaining intestinal homeostasis VSports手机版. Therefore, dysregulation within the epithelial layer can increase intestinal permeability, lead to abnormalities in interactions between IECs and immune cells in underlying lamina propria, and disturb the intestinal immune homeostasis, all of which are linked to the clinical disease course of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Understanding the role of the intestinal epithelium in IBD pathogenesis might contribute to an improved knowledge of the inflammatory processes and the identification of potential therapeutic targets. .
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; barrier dysfunction; inflammatory bowel disease; intestinal epithelium; tight junctions; ulcerative colitis. V体育安卓版.
Figures
References
-
- Kaser A, Zeissig S, Blumberg RS. Inflammatory bowel disease. Annu Rev Immunol (2010) 28:573–621.10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101225 - V体育2025版 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types (V体育2025版)
V体育安卓版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"VSports最新版本" Medical