Macrophage-derived human resistin is induced in multiple helminth infections and promotes inflammatory monocytes and increased parasite burden (V体育安卓版)
- PMID: 25568944
- PMCID: PMC4287580
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004579
Macrophage-derived human resistin is induced in multiple helminth infections and promotes inflammatory monocytes and increased parasite burden
Abstract (VSports注册入口)
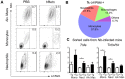
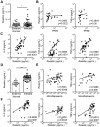
Parasitic helminth infections can be associated with lifelong morbidity such as immune-mediated organ failure VSports手机版. A better understanding of the host immune response to helminths could provide new avenues to promote parasite clearance and/or alleviate infection-associated morbidity. Murine resistin-like molecules (RELM) exhibit pleiotropic functions following helminth infection including modulating the host immune response; however, the relevance of human RELM proteins in helminth infection is unknown. To examine the function of human resistin (hResistin), we utilized transgenic mice expressing the human resistin gene (hRetnTg+). Following infection with the helminth Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nb), hResistin expression was significantly upregulated in infected tissue. Compared to control hRetnTg- mice, hRetnTg+ mice suffered from exacerbated Nb-induced inflammation characterized by weight loss and increased infiltration of inflammatory monocytes in the lung, along with elevated Nb egg burdens and delayed parasite expulsion. Genome-wide transcriptional profiling of the infected tissue revealed that hResistin promoted expression of proinflammatory cytokines and genes downstream of toll-like receptor signaling. Moreover, hResistin preferentially bound lung monocytes, and exogenous treatment of mice with recombinant hResistin promoted monocyte recruitment and proinflammatory cytokine expression. In human studies, increased serum resistin was associated with higher parasite load in individuals infected with soil-transmitted helminths or filarial nematode Wuchereria bancrofti, and was positively correlated with proinflammatory cytokines. Together, these studies identify human resistin as a detrimental factor induced by multiple helminth infections, where it promotes proinflammatory cytokines and impedes parasite clearance. Targeting the resistin/proinflammatory cytokine immune axis may provide new diagnostic or treatment strategies for helminth infection and associated immune-mediated pathology. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- MacDonald TT, Choy MY, Spencer J, Richman PI, Diss T, et al. (1991) Histopathology and immunohistochemistry of the caecum in children with the Trichuris dysentery syndrome. J Clin Pathol 44: 194–199. - V体育平台登录 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neill DR, Wong SH, Bellosi A, Flynn RJ, Daly M, et al. (2010) Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature 464: 1367–1370. - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
-
- Voehringer D, Shinkai K, Locksley RM (2004) Type 2 immunity reflects orchestrated recruitment of cells committed to IL-4 production. Immunity 20: 267–277. - PubMed
"V体育ios版" Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
Substances
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Grants and funding
- 088862/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- S10 RR028934/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 100714/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 1R01AI091759-01A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 088862/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 1S10RR028934-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK049210/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States (V体育ios版)
- P01DK49210/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10OD016290-01A1/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091759/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD016290/OD/NIH HHS/United States
VSports最新版本 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports最新版本)
Molecular Biology Databases

