Large-scale topology and the default mode network in the mouse connectome
- PMID: 25512496
- PMCID: PMC4284535
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1404346111
"V体育2025版" Large-scale topology and the default mode network in the mouse connectome
Abstract
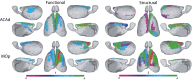
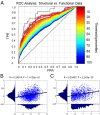
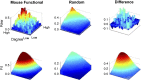
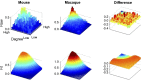
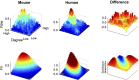
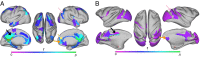
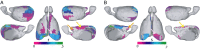
Noninvasive functional imaging holds great promise for serving as a translational bridge between human and animal models of various neurological and psychiatric disorders. However, despite a depth of knowledge of the cellular and molecular underpinnings of atypical processes in mouse models, little is known about the large-scale functional architecture measured by functional brain imaging, limiting translation to human conditions. Here, we provide a robust processing pipeline to generate high-resolution, whole-brain resting-state functional connectivity MRI (rs-fcMRI) images in the mouse VSports手机版. Using a mesoscale structural connectome (i. e. , an anterograde tracer mapping of axonal projections across the mouse CNS), we show that rs-fcMRI in the mouse has strong structural underpinnings, validating our procedures. We next directly show that large-scale network properties previously identified in primates are present in rodents, although they differ in several ways. Last, we examine the existence of the so-called default mode network (DMN)--a distributed functional brain system identified in primates as being highly important for social cognition and overall brain function and atypically functionally connected across a multitude of disorders. We show the presence of a potential DMN in the mouse brain both structurally and functionally. Together, these studies confirm the presence of basic network properties and functional networks of high translational importance in structural and functional systems in the mouse brain. This work clears the way for an important bridge measurement between human and rodent models, enabling us to make stronger conclusions about how regionally specific cellular and molecular manipulations in mice relate back to humans. .
Keywords: connectivity; default mode network; mouse; resting-state functional MRI; structural connectivity. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
"V体育平台登录" References
-
- Logothetis NK. Intracortical recordings and fMRI: An attempt to study operational modules and networks simultaneously. Neuroimage. 2012;62(2):962–969. - PubMed
-
- Fair DA, et al. The maturing architecture of the brain’s default network. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(10):4028–4032. - "V体育平台登录" PMC - PubMed
-
- Hagmann P, et al. White matter maturation reshapes structural connectivity in the late developing human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(44):19067–19072. - "V体育安卓版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Grayson DS, et al. Structural and functional rich club organization of the brain in children and adults. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(2):e88297. - VSports注册入口 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Martino A, et al. Detection of functional connectivity in the resting mouse brain. Neuroimage. 2014;86:417–424. - "VSports手机版" PubMed
V体育官网 - Publication types
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

