m(6)A RNA modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells (V体育ios版)
- PMID: 25456834
- PMCID: PMC4278749 (V体育官网)
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.09.019
"VSports app下载" m(6)A RNA modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells
Abstract
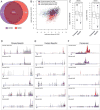
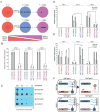
N6-methyl-adenosine (m(6)A) is the most abundant modification on messenger RNAs and is linked to human diseases, but its functions in mammalian development are poorly understood. Here we reveal the evolutionary conservation and function of m(6)A by mapping the m(6)A methylome in mouse and human embryonic stem cells VSports手机版. Thousands of messenger and long noncoding RNAs show conserved m(6)A modification, including transcripts encoding core pluripotency transcription factors. m(6)A is enriched over 3' untranslated regions at defined sequence motifs and marks unstable transcripts, including transcripts turned over upon differentiation. Genetic inactivation or depletion of mouse and human Mettl3, one of the m(6)A methylases, led to m(6)A erasure on select target genes, prolonged Nanog expression upon differentiation, and impaired ESC exit from self-renewal toward differentiation into several lineages in vitro and in vivo. Thus, m(6)A is a mark of transcriptome flexibility required for stem cells to differentiate to specific lineages. .
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc V体育安卓版. All rights reserved. .
Figures (VSports app下载)

Comment in
-
Stem cell RNA epigenetics: m(6)arking your territory.Cell Stem Cell. 2014 Dec 4;15(6):669-70. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.11.011. Cell Stem Cell. 2014. PMID: 25479740
References (VSports最新版本)
-
- Bodi Z, Zhong S, Mehra S, Song J, Graham N, Li H, May S, Fray RG. Adenosine Methylation in Arabidopsis mRNA is Associated with the 3′ End and Reduced Levels Cause Developmental Defects. Front Plant Sci. 2012;3:48. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Dawlaty MM, Ganz K, Powell BE, Hu YC, Markoulaki S, Cheng AW, Gao Q, Kim J, Choi SW, Page DC, et al. Tet1 is dispensable for maintaining pluripotency and its loss is compatible with embryonic and postnatal development. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9:166–175. - PMC (V体育ios版) - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K, Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–206. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网)
MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Grants and funding (VSports最新版本)
"VSports最新版本" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
V体育平台登录 - Research Materials

