The thymoquinone-induced production of reactive oxygen species promotes dedifferentiation through the ERK pathway and inflammation through the p38 and PI3K pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes
- PMID: 25435376
- PMCID: PMC4292767
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.2014
VSports - The thymoquinone-induced production of reactive oxygen species promotes dedifferentiation through the ERK pathway and inflammation through the p38 and PI3K pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes
VSports - Abstract
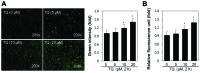
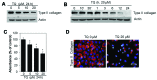
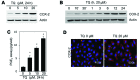
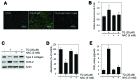
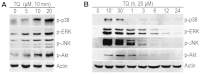
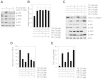
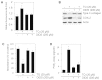
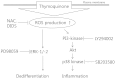
Dedifferentiation and inflammation are major features of cartilage degeneration during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA) VSports手机版. Thymoquinone (TQ) is the major compound of black seed oil isolated from Nigella sativa with various beneficial or harmful effects on several diseases; however, its effects on the dedifferentiation and inflammation of chondrocytes have not yet been characterized. In the present study, we investigated whether TQ regulates the dedifferentiation and inflammation of rabbit articular chondrocytes, focusing on the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in rabbit articular chondrocytes. TQ induced the generation of ROS in a dose-dependent manner, as shown by staining with the fluorescent probe, 2'-7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate. We confirmed that TQ induced dedifferentiation by measuring the loss of type II collagen and the reduction in chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan levels. TQ also caused inflammation by inducing the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The antioxidant, N-acetyl cysteine (NAC), prevented the dedifferentiation and inflammation which was generated by the TQ-induced production of ROS. Furthermore, TQ caused a dose-dependent increase in p38, phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) expression. NAC abrogated this effect and attenuated the dedifferentiation and inflammation which was generated by the TQ-induced production of ROS. To identify the ROS-regulated pathways, we treated the chondrocytes with the p38 inhibitor, SB203580, the MEK inhibitor, PD98059, and the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002. PD98059 inhibited the TQ-induced dedifferentiation and SB203580 and LY294002 prevented the TQ-induced inflammation. These findings suggest that the TQ-induced production of ROS causes dedifferentiation through the ERK pathway and inflammation through the PI3K and p38 pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes. .
Figures
References
-
- Goldring MB, Tsuchimochi K, Ijiri K. The control of chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97:33–44. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20652. - "VSports在线直播" DOI - PubMed
"V体育安卓版" Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
Substances
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
V体育安卓版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

