FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis
- PMID: 25412662
- PMCID: PMC4260349
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2014.151
FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis
Abstract
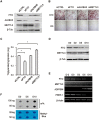
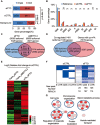
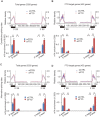
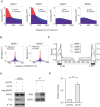
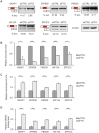
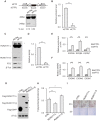
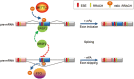
The role of Fat Mass and Obesity-associated protein (FTO) and its substrate N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in mRNA processing and adipogenesis remains largely unknown VSports手机版. We show that FTO expression and m6A levels are inversely correlated during adipogenesis. FTO depletion blocks differentiation and only catalytically active FTO restores adipogenesis. Transcriptome analyses in combination with m6A-seq revealed that gene expression and mRNA splicing of grouped genes are regulated by FTO. M6A is enriched in exonic regions flanking 5'- and 3'-splice sites, spatially overlapping with mRNA splicing regulatory serine/arginine-rich (SR) protein exonic splicing enhancer binding regions. Enhanced levels of m6A in response to FTO depletion promotes the RNA binding ability of SRSF2 protein, leading to increased inclusion of target exons. FTO controls exonic splicing of adipogenic regulatory factor RUNX1T1 by regulating m6A levels around splice sites and thereby modulates differentiation. These findings provide compelling evidence that FTO-dependent m6A demethylation functions as a novel regulatory mechanism of RNA processing and plays a critical role in the regulation of adipogenesis. .
Figures
Comment in
-
FTO: linking m6A demethylation to adipogenesis.Cell Res. 2015 Jan;25(1):3-4. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.162. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25475057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Loos RJ, Bouchard C. FTO: the first gene contributing to common forms of human obesity. Obes Rev. 2008;9:246–250. - "VSports app下载" PubMed
-
- Zabena C, Gonzalez-Sanchez JL, Martinez-Larrad MT, et al. The FTO obesity gene. Genotyping and gene expression analysis in morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg. 2009;19:87–95. - PubMed
-
- Fischer J, Koch L, Emmerling C, et al. Inactivation of the Fto gene protects from obesity. Nature. 2009;458:894–898. - V体育ios版 - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
"V体育平台登录" Substances
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
"VSports最新版本" Associated data
- "V体育官网" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"VSports手机版" Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

