Stabilization of HIF through inhibition of Cullin-2 neddylation is protective in mucosal inflammatory responses
- PMID: 25326537
- PMCID: PMC4285538
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.14-259663
Stabilization of HIF through inhibition of Cullin-2 neddylation is protective in mucosal inflammatory responses
Abstract
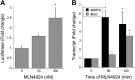
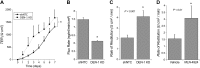
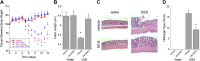
There is interest in understanding post-translational modifications of proteins in inflammatory disease. Neddylation is the conjugation of the molecule neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 8 (NEDD8) to promote protein stabilization VSports手机版. Cullins are a family of NEDD8 targets important in the stabilization and degradation of proteins, such as hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF; via Cullin-2). Here, we elucidate the role of human deneddylase-1 (DEN-1, also called SENP8) in inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo and define conditions for targeting neddylation in models of mucosal inflammation. HIF provides protection in inflammatory models, so we examined the contribution of DEN-1 to HIF stabilization. Pharmacologic targeting of neddylation activity with MLN4924 (IC50, 4. 7 nM) stabilized HIF-1α, activated HIF promoter activity by 2. 5-fold, and induced HIF-target genes in human epithelial cells up to 5-fold. Knockdown of DEN-1 in human intestinal epithelial cells resulted in increased kinetics in barrier formation, decreased permeability, and enhanced barrier restitution by 2 ± 0. 5-fold. Parallel studies in vivo revealed that MLN4924 abrogated disease severity in murine dextran sulfate sodium colitis, including weight loss, colon length, and histologic severity. We conclude that DEN-1 is a regulator of cullin neddylation and fine-tunes the inflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. Pharmacologic inhibition of cullin neddylation may provide a therapeutic opportunity in mucosal inflammatory disease. .
Keywords: hypoxia; inflammation; intestinal epithelia. V体育安卓版.
© FASEB.
Figures
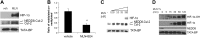

References
-
- Xavier R. J., Podolsky D. K. (2007) Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 448, 427–434 - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Ehrentraut S. F., Colgan S. P. (2012) Implications of protein post-translational modifications in IBD. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 18, 1378–1388 - V体育ios版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xirodimas D. P. (2008) Novel substrates and functions for the ubiquitin-like molecule NEDD8. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36, 802–806 - PubMed
-
- Mikus P., Zundel W. (2005) COPing with hypoxia. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 16, 462–473 - PMC (VSports手机版) - PubMed
-
- Read M. A., Brownell J. E., Gladysheva T. B., Hottelet M., Parent L. A., Coggins M. B., Pierce J. W., Podust V. N., Luo R. S., Chau V., Palombella V. J. (2000) Nedd8 modification of cul-1 activates SCF(beta(TrCP))-dependent ubiquitination of IkappaBalpha. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 2326–2333 - PMC (V体育ios版) - PubMed
Publication types (V体育ios版)
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
Grants and funding
- "V体育安卓版" R01 DK103639/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008497/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States (VSports在线直播)
- HL60569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports最新版本" R01 DK104713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- "V体育平台登录" R01 DK103712/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R29 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK95491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports手机版" I01 BX002182/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R37 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK095491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK50189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育ios版" Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

