Tumor suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: mechanisms and opportunities
- PMID: 25314076
- PMCID: PMC4227608
- DOI: "V体育官网" 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.013
Tumor suppression by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase: mechanisms and opportunities
Abstract
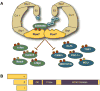
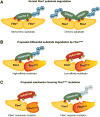
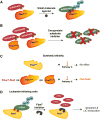
Tumor suppressors with widespread impact on carcinogenesis control broad spectra of oncogenic pathways. Protein degradation is an emerging mechanism by which tumor suppressors regulate a diversity of pathways and is exemplified by the SCF(Fbw7) ubiquitin ligase. Rapidly accumulating data indicate that SCF(Fbw7) regulates a network of crucial oncoproteins. Importantly, the FBXW7 gene, which encodes Fbw7, is one of the most frequently mutated genes in human cancers. These studies are yielding important new insights into tumorigenesis and may soon enable therapies targeting the Fbw7 pathway VSports手机版. Here, we focus on the mechanisms and consequences of Fbw7 deregulation in cancers and discuss possible therapeutic approaches. .
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved V体育安卓版. .
Figures
References
-
- Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N, Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, Cepeda D, Fiegl H, Dafou D, Marth C, et al. FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer research. 2007;67:9006–9012. - PubMed
-
- Babaei-Jadidi R, Li N, Saadeddin A, Spencer-Dene B, Jandke A, Muhammad B, Ibrahim EE, Muraleedharan R, Abuzinadah M, Davis H, et al. FBXW7 influences murine intestinal homeostasis and cancer, targeting Notch, Jun, and DEK for degradation. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2011;208:295–312. - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
-
- Bahram F, von der Lehr N, Cetinkaya C, Larsson LG. c-Myc hot spot mutations in lymphomas result in inefficient ubiquitination and decreased proteasome-mediated turnover. Blood. 2000;95:2104–2110. - PubMed
-
- Balamurugan K, Sharan S, Klarmann KD, Zhang Y, Coppola V, Summers GH, Roger T, Morrison DK, Keller JR, Sterneck E. FBXW7alpha attenuates inflammatory signalling by downregulating C/EBPdelta and its target gene Tlr4. Nature communications. 2013;4:1662. - "VSports" PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
Substances
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
VSports手机版 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育官网" Molecular Biology Databases

