The possible role of the novel cytokines il-35 and il-37 in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 25214710
- PMCID: "VSports" PMC4151582
- DOI: "V体育官网" 10.1155/2014/136329
VSports在线直播 - The possible role of the novel cytokines il-35 and il-37 in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract (VSports)
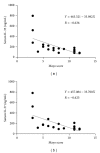
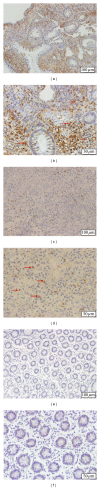
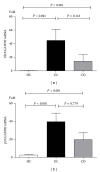
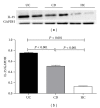
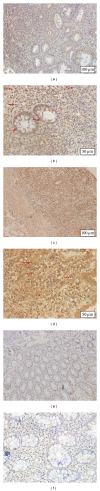
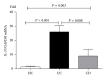
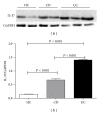
Interleukin- (IL-) 35 and IL-37 are newly discovered immune-suppressing cytokines. They have been described in inflammatory diseases such as collagen-induced arthritis and asthma. However, their expressions in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients have not been yet explored. Our aim was to evaluate serum and inflamed mucosal levels in IBD patients. In 20 ulcerative colitis (UC) patients, 7 Crohn's disease (CD) patients, and 15 healthy subjects, cytokine levels in serum were determined using ELISA and mucosal expression studies were performed by immunohistochemistry, quantitative real-time PCR, and Western blot. The results showed that serums IL-35 and IL-37 levels were significantly decreased in UC and CD patients compared with healthy subjects VSports手机版. The cytokines levels correlated inversely with UC activity. IL-35 was expressed in infiltrating immune cells while IL-37 in intestinal epithelial cells as well as inflammatory cells. IBD patients had significantly higher Ebi3, p35 (two subunits of IL-35), and IL-37b gene expressions; IL-35 and IL-37 protein expressions were higher in IBD patients compared with controls. The study showed that serums IL-35 and IL-37 might be potentially novel biomarkers for IBD. Intestinal IL-35 and IL-37 proteins are upregulated, suggesting that regulating the expression of the two cytokines may provide a new possible target for the treatment of IBD. .
Figures
References
-
- Podolsky DK. Inflammatory bowel disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;347(6):417–429. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
-
- MacDonald TT, Monteleone G. Immunity, inflammation, and allergy in the gut. Science. 2005;307(5717):1920–1925. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
-
- Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2011;474(7351):298–306. - PubMed
-
- Collison LW, Workman CJ, Kuo TT, et al. The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature. 2007;450(7169):566–569. - PubMed
MeSH terms
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育ios版" Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

