Somatostatin regulates tight junction proteins expression in colitis mice
- PMID: 24966923
- PMCID: V体育2025版 - PMC4069911
VSports注册入口 - Somatostatin regulates tight junction proteins expression in colitis mice
"VSports app下载" Abstract
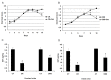
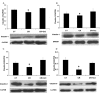
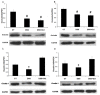
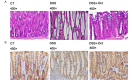
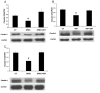
Tight junction plays a critical role in intestinal defence. The alteration and perturbation of tight junction proteins could induce intestine barrier damage, and lead to the malabsorption of electrolytes and water. Previous studies had showed that colonic infection and inflammation could lead to the alteration of tight junction function, and somatostatin could protect intestinal epithelia. Thus, this study could explore that whether somatostatin could regulate tight junction in colitis mice. Colitis mice with diarrhea were induced by Citrobacter rodentium (CR) and Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) VSports手机版. In CR infected model, cladudin-1 and claudin-3 expression significantly decreased compared with the control mice (P<0. 05); after octreotide treatment, claudin-1 and claudin-3 expression significantly increased compared with untreated CR infected mice (P<0. 05). In DSS colitis model, occludin and claudin-3 expression significantly decreased compared with the control mice (P<0. 05); and octreotide treatment could only significantly upregulate claudin-3 expression compared with untreated DSS colitis mice (P<0. 05). To testify our results in vivo, we repeated the models in caco-2 cells by exposed with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (E. Coli) and Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α). The results in vitro were consistent with in vivo study. The results suggested that somatostatin play a role in intestinal barrier protection by modulating tight junction proteins expression. .
Keywords: IBD; Tight junction; claudins; infectious colitis; occludin; somatostatin. V体育安卓版.
Figures
References
-
- González-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE. Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2003;81:1–44. - VSports注册入口 - PubMed
-
- Guttman JA, Li Y, Wickham ME, Deng W, Vogl AW, Finlay BB. Attaching and effacing pathogen-induced tight junction disruption in vivo. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:634–45. - PubMed (V体育2025版)
-
- Guttman JA, Finlay BB. Tight junctions as targets of infectious agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1788:832–841. - PubMed
-
- Vetrano S, Rescigno M, Cera MR, Correale C, Rumio C, Doni A, Fantini M, Sturm A, Borroni E, Repici A, Locati M, Malesci A, Dejana E, Danese S. Unique role of junctional adhesion molecule-a in maintaining mucosal homeostasis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:173–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
VSports - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
