Prognostic significance of the co-overexpression of fibroblast growth factor receptors 1, 2 and 4 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 24940486
- PMCID: PMC4051553
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2014.293
VSports - Prognostic significance of the co-overexpression of fibroblast growth factor receptors 1, 2 and 4 in gastric cancer
Abstract
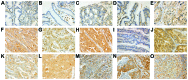
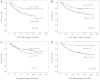
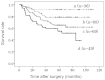
The overexpression of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 2 is an established prognostic factor and treatment target in gastric cancer. However, the roles of other FGFRs have not been fully elucidated. In this study, we investigated the correlations of the expression of FGFR1-4 with clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes in gastric cancer. Tumor samples were obtained from 222 patients with gastric adenocarcinoma who underwent gastrectomy between 2003 and 2007. The expression of each FGFR was measured in the tumors by immunohistochemical analysis. The overexpression of FGFR1, FGFR2 or FGFR4 was found to be significantly associated with tumor progression, including depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis, pathological stage and distant metastasis or recurrent disease. Patients exhibiting overexpression of FGFR1, FGFR2 or FGFR4 had a significantly poorer disease-specific survival (DSS; P<0. 001, P=0. 008 and P<0. 001, respectively). Moreover, the co-overexpression of all three FGFRs was significantly associated with a poorer DSS compared to the expression of none or only one of the FGFRs (P<0. 001 and P=0. 001, respectively) and it was found to be an independent prognostic factor (HR=1. 71, 95% CI: 1. 02-2. 85, P=0. 041). In conclusion, high expression of FGFR1, FGFR2 or FGFR4 was associated with tumor progression and poor survival in patients with gastric cancer VSports手机版. Similar to FGFR2, FGFR1 and FGFR4 may be considered as prognostic factors and treatment targets in gastric cancer. .
Keywords: fibroblast growth factor receptor; gastric cancer; immunohistochemical analysis V体育安卓版. .
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- Brenner H, Rothenbacher D, Arndt V. Epidemiology of stomach cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;472:467–477. - PubMed (V体育平台登录)
-
- Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:36–46. - PubMed
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:687–697. - PubMed (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports app下载" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
