Unifying the analysis of high-throughput sequencing datasets: characterizing RNA-seq, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and selective growth experiments by compositional data analysis
- PMID: 24910773
- PMCID: PMC4030730
- DOI: "VSports手机版" 10.1186/2049-2618-2-15
Unifying the analysis of high-throughput sequencing datasets: characterizing RNA-seq, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and selective growth experiments by compositional data analysis
Abstract (VSports)
Background: Experimental designs that take advantage of high-throughput sequencing to generate datasets include RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq), sequencing of 16S rRNA gene fragments, metagenomic analysis and selective growth experiments. In each case the underlying data are similar and are composed of counts of sequencing reads mapped to a large number of features in each sample. Despite this underlying similarity, the data analysis methods used for these experimental designs are all different, and do not translate across experiments. Alternative methods have been developed in the physical and geological sciences that treat similar data as compositions. Compositional data analysis methods transform the data to relative abundances with the result that the analyses are more robust and reproducible. VSports手机版.
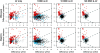
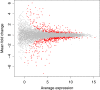
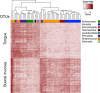
Results: Data from an in vitro selective growth experiment, an RNA-seq experiment and the Human Microbiome Project 16S rRNA gene abundance dataset were examined by ALDEx2, a compositional data analysis tool that uses Bayesian methods to infer technical and statistical error V体育安卓版. The ALDEx2 approach is shown to be suitable for all three types of data: it correctly identifies both the direction and differential abundance of features in the differential growth experiment, it identifies a substantially similar set of differentially expressed genes in the RNA-seq dataset as the leading tools and it identifies as differential the taxa that distinguish the tongue dorsum and buccal mucosa in the Human Microbiome Project dataset. The design of ALDEx2 reduces the number of false positive identifications that result from datasets composed of many features in few samples. .
Conclusion: Statistical analysis of high-throughput sequencing datasets composed of per feature counts showed that the ALDEx2 R package is a simple and robust tool, which can be applied to RNA-seq, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and differential growth datasets, and by extension to other techniques that use a similar approach. V体育ios版.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene sequencing; Dirichlet distribution; Monte Carlo sampling; RNA-seq; centered log-ratio transformation; compositional data; differential abundance; high-throughput sequencing; microbiome VSports最新版本. .
Figures

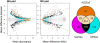
"VSports手机版" References
-
- Anders S, McCarthy DJ, Chen Y, Okoniewski M, Smyth GK, Huber W, Robinson MD. Count-based 631 differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data using R and Bioconductor. Nat Protoc. 2013;8(9):1765–86. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.099. - "VSports手机版" DOI - PubMed
-
- Dillies M-A, Rau A, Aubert J, Hennequet-Antier C, Jeanmougin M, Servant N, Keime C, Marot G, Castel D, Estelle J, Guernec G, Jagla B, Jouneau L, Laloë D, Le Gall C, Schaëffer B, Le Crom S, Guedj M, Jaffrëzic F. on behalf of the French StatOmique Consortium. A comprehensive evaluation of normalizationmethods for Illumina high-throughput RNA sequencing data analysis. Brief Bioinform. 2013;14(6):671–83. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs046. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75(23):7537–41. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01541-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R. Qiime allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 2010;7(5):335–6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育官网入口)
Other Literature Sources (VSports最新版本)
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

