Pharmacokinetics, clearance, and biosafety of polyethylene glycol-coated hollow gold nanospheres
- PMID: 24886070
- PMCID: PMC4082425
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-8977-11-26
Pharmacokinetics, clearance, and biosafety of polyethylene glycol-coated hollow gold nanospheres
VSports手机版 - Abstract
Objective: Gold nanoparticles have attracted enormous interest as potential theranostic agents. However, little is known about the long-term elimination and systemic toxicity of gold nanoparticles in the literature. Hollow gold nanospheres (HAuNS) is a class of photothermal conducting agent that have shown promises in photoacoustic imaging, photothermal ablation therapy, and drug delivery. It's very necessary to make clear the biosafety of HAuNS for its further application. VSports手机版.
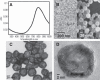
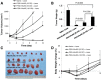
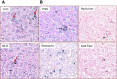
Methods: We investigated the cytotoxicity, complement activation, and platelet aggregation of polyethylene glycol (PEG)-coated HAuNS (PEG-HAuNS, average diameter of 63 nm) in vitro and their pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, organ elimination, hematology, clinical chemistry, acute toxicity, and chronic toxicity in mice V体育安卓版. .
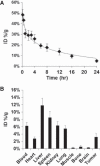
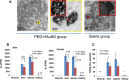
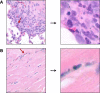
Results: PEG-HAuNS did not induce detectable activation of the complement system and did not induce detectable platelet aggregation. The blood half-life of PEG-HAuNS in mice was 8. 19 ± 1 V体育ios版. 4 hr. The single effective dose of PEG-HAuNS in photothermal ablation therapy was determined to be 12. 5 mg/kg. PEG-HAuNS caused no adverse effects after 10 daily intravenous injections over a 2-week period at a dose of 12. 5 mg/kg per injection (accumulated dose: 125 mg/kg). Quantitative analysis of the muscle, liver, spleen, and kidney revealed that the levels of Au decreased 45. 2%, 28. 6%, 41. 7%, and 40. 8%, respectively, from day 14 to day 90 after the first intravenous injection, indicating that PEG-HAuNS was slowly cleared from these organs in mice. .
Conclusion: Our data support the use of PEG-HAuNS as a promising photothermal conducting agent VSports最新版本. .
Figures (V体育官网入口)

"V体育平台登录" References
-
- Caruthers SD, Wickline SA, Lanza GM. Nanotechnological applications in medicine. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2007;18:26–30. - PubMed (V体育安卓版)
-
- Li C. A targeted approach to cancer imaging and therapy. Nat Mater. 2014;13:110–115. - "V体育安卓版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Guzman KAD, Taylor MR, Banfield JF. Environmental risks of nanotechnology: national nanotechnology initiative funding, 2000–2004. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40:1401–1407. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Borm PJA, Muller-Schulte D. Nanoparticles in drug delivery and environmental exposure: same size, same risks? Nanomedicine. 2006;1:235–249. - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
-
- Carrero-Sanchez JC, Elias AL, Mancilla R, Arrellin G, Terrones H, Laclette JP, Terrones M. Biocompatibility and toxicological studies of carbon nanotubes doped with nitrogen. Nano Lett. 2006;6:1609–1616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
Grants and funding
"VSports app下载" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

