Natural rice rhizospheric microbes suppress rice blast infections
- PMID: 24884531
- PMCID: PMC4036093
- DOI: V体育官网 - 10.1186/1471-2229-14-130
Natural rice rhizospheric microbes suppress rice blast infections
Abstract (VSports注册入口)
Background: The natural interactions between plant roots and their rhizospheric microbiome are vital to plant fitness, modulating both growth promotion and disease suppression VSports手机版. In rice (Oryza sativa), a globally important food crop, as much as 30% of yields are lost due to blast disease caused by fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Capitalizing on the abilities of naturally occurring rice soil bacteria to reduce M. oryzae infections could provide a sustainable solution to reduce the amount of crops lost to blast disease. .
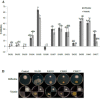
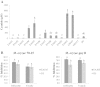
Results: Naturally occurring root-associated rhizospheric bacteria were isolated from California field grown rice plants (M-104), eleven of which were taxonomically identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) analysis V体育安卓版. Bacterial isolates were tested for biocontrol activity against the devastating foliar rice fungal pathogen, M. oryzae pathovar 70-15. In vitro, a Pseudomonas isolate, EA105, displayed antibiosis through reducing appressoria formation by nearly 90% as well as directly inhibiting fungal growth by 76%. Although hydrogen cyanide (HCN) is a volatile commonly produced by biocontrol pseudomonads, the activity of EA105 seems to be independent of its HCN production. During in planta experiments, EA105 reduced the number of blast lesions formed by 33% and Pantoea agglomerans isolate, EA106 by 46%. Our data also show both EA105 and EA106 trigger jasmonic acid (JA) and ethylene (ET) dependent induced systemic resistance (ISR) response in rice. .
Conclusions: Out of 11 bacteria isolated from rice soil, pseudomonad EA105 most effectively inhibited the growth and appressoria formation of M. oryzae through a mechanism that is independent of cyanide production V体育ios版. In addition to direct antagonism, EA105 also appears to trigger ISR in rice plants through a mechanism that is dependent on JA and ET signaling, ultimately resulting in fewer blast lesions. The application of native bacteria as biocontrol agents in combination with current disease protection strategies could aid in global food security. .
Figures





References
-
- Zeigler RS, Leong SA, Teng PS. Rice blast disease. Rice Blast Disease. 1994. pp. 1–626.
-
- Bonman JM, Khush GS, Nelson RJ. Breeding rice for resistance to pests. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 1992;30:507–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.30.090192.002451. - DOI
-
- Chuma I, Isobe C, Hotta Y, Ibaragi K, Futamata N, Kusaba M, Yoshida K, Terauchi R, Fujita Y, Nakayashiki H, Valent B, Tosa Y. Multiple translocation of the AVR-Pita effector gene among chromosomes of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae and related species. PLoS Pathogens. 2011;7:e1002147. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002147. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
VSports注册入口 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

