Activating and propagating polyclonal gamma delta T cells with broad specificity for malignancies
- PMID: 24833662
- PMCID: PMC4233015
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3451
Activating and propagating polyclonal gamma delta T cells with broad specificity for malignancies
V体育官网 - Abstract
Purpose: To activate and propagate populations of γδ T cells expressing polyclonal repertoire of γ and δ T-cell receptor (TCR) chains for adoptive immunotherapy of cancer, which has yet to be achieved. VSports手机版.
Experimental design: Clinical-grade artificial antigen-presenting cells (aAPC) derived from K562 tumor cells were used as irradiated feeders to activate and expand human γδ T cells to clinical scale. These cells were tested for proliferation, TCR expression, memory phenotype, cytokine secretion, and tumor killing V体育安卓版. .
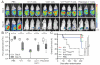
Results: γδ T-cell proliferation was dependent upon CD137L expression on aAPC and addition of exogenous IL2 and IL21. Propagated γδ T cells were polyclonal as they expressed TRDV1, TRDV2-2, TRDV3, TRDV5, TRDV7, and TRDV8 with TRGV2, TRGV3F, TRGV7, TRGV8, TRGV9*A1, TRGV10*A1, and TRGV11 TCR chains. IFNγ production by Vδ1, Vδ2, and Vδ1(neg)Vδ2(neg) subsets was inhibited by pan-TCRγδ antibody when added to cocultures of polyclonal γδ T cells and tumor cell lines. Polyclonal γδ T cells killed acute and chronic leukemia, colon, pancreatic, and ovarian cancer cell lines, but not healthy autologous or allogeneic normal B cells. Blocking antibodies demonstrated that polyclonal γδ T cells mediated tumor cell lysis through combination of DNAM1, NKG2D, and TCRγδ. The adoptive transfer of activated and propagated γδ T cells expressing polyclonal versus defined Vδ TCR chains imparted a hierarchy (polyclonal>Vδ1>Vδ1(neg)Vδ2(neg)>Vδ2) of survival of mice with ovarian cancer xenografts. V体育ios版.
Conclusions: Polyclonal γδ T cells can be activated and propagated with clinical-grade aAPCs and demonstrate broad antitumor activities, which will facilitate the implementation of γδ T-cell cancer immunotherapies in humans VSports最新版本. .
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research. V体育平台登录.
Figures



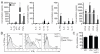

Comment in
-
VSports - Promising cell-based immunotherapy using gamma delta T cells: together is better.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Nov 15;20(22):5573-5. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1371. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25278452
"VSports app下载" References
-
- Bonneville M, O’Brien RL, Born WK. Gammadelta T cell effector functions: a blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:467–78. - PubMed
-
- Lefranc MP. Nomenclature of the human T cell receptor genes. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2001 Appendix 1:Appendix 1O. - "V体育平台登录" PubMed
-
- Turchinovich G, Pennington DJ. T cell receptor signalling in gammadelta cell development: strength isn’t everything. Trends Immunol. 2011;32:567–73. - PubMed
-
- Kabelitz D, Wesch D, He W. Perspectives of gammadelta T cells in tumor immunology. Cancer Res. 2007;67:5–8. - VSports app下载 - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Grants and funding (VSports注册入口)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育ios版)
Research Materials (VSports手机版)

