Normalyzer: a tool for rapid evaluation of normalization methods for omics data sets
- PMID: 24766612
- PMCID: "V体育官网入口" PMC4053077
- DOI: 10.1021/pr401264n
"V体育官网" Normalyzer: a tool for rapid evaluation of normalization methods for omics data sets
Abstract
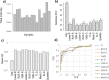
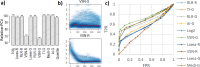
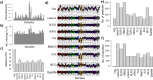
High-throughput omics data often contain systematic biases introduced during various steps of sample processing and data generation. As the source of these biases is usually unknown, it is difficult to select an optimal normalization method for a given data set. To facilitate this process, we introduce the open-source tool "Normalyzer". It normalizes the data with 12 different normalization methods and generates a report with several quantitative and qualitative plots for comparative evaluation of different methods. The usefulness of Normalyzer is demonstrated with three different case studies from quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics. The results from these case studies show that the choice of normalization method strongly influences the outcome of downstream quantitative comparisons. Normalyzer is an R package and can be used locally or through the online implementation at http://quantitativeproteomics. org/normalyzer . VSports手机版.
Figures

References
-
- Karpievitch Y. V.; Dabney A. R.; Smith R. D. Normalization and missing value imputation for label-free LC-MS analysis. BMC Bioinf. 2012, 13Suppl 16S5. - "VSports在线直播" PMC - PubMed
-
- Craig A.; Cloarec O.; Holmes E.; Nicholson J. K.; Lindon J. C. Scaling and normalization effects in NMR spectroscopic metabonomic data sets. Anal. Chem. 2006, 7872262–7. - PubMed
-
- Callister S. J.; Barry R. C.; Adkins J. N.; Johnson E. T.; Qian W. J.; Webb-Robertson B. J.; Smith R. D.; Lipton M. S. Normalization approaches for removing systematic biases associated with mass spectrometry and label-free proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 52277–86. - PMC (VSports) - PubMed
"V体育2025版" Publication types
MeSH terms (VSports手机版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
VSports最新版本 - Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

