Expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/CCL2 in gastric cancer and its relationship with tumor hypoxia
- PMID: 24764682
- PMCID: "V体育平台登录" PMC3989980
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4421 (VSports在线直播)
Expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/CCL2 in gastric cancer and its relationship with tumor hypoxia
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the expression and prognostic value of CCL2 in gastric cancer, as well as its relationship with tumor hypoxia VSports手机版. .
Methods: Tumor tissues from 68 gastric cancer patients (GC) were analyzed, and the expression of CCL2 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) in tumor tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry. Statistical evaluations that were used included univariate log-rank tests of Kaplan-Meier curves and multivariate Cox regression model analysis V体育安卓版. .
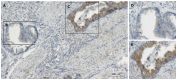
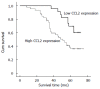
Results: CCL2 was highly expressed in 66 V体育ios版. 2% (45/68) of gastric cancer specimens. The distribution of CCL2 expression in tumor tissue was consistent with that of HIF-1α. Patients with high CCL2 expression in GC had a lower overall survival rate [50. 6 mo (95%CI: 44. 44-56. 93) vs 64. 6 mo (95%CI: 60. 27-68. 94), P = 0. 013]. .
Conclusion: CCL2 expression correlates closely with HIF-1α expression in gastric cancer. CCL2 may be an independent prognostic marker for GC. VSports最新版本.
Keywords: Chemokines; Gastric cancer; Immunohistochemistry; Monocyte chemotactic protein-1/CCL2; Prognostic marker V体育平台登录. .
Figures

References
-
- de Martel C, Forman D, Plummer M. Gastric cancer: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013;42:219–240. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
-
- Guggenheim DE, Shah MA. Gastric cancer epidemiology and risk factors. J Surg Oncol. 2013;107:230–236. - "VSports" PubMed
-
- Kumar RK, Shankar EM, Ganapathy E, Raj SS, Ebrahim AS, Farooq SM. Gastric Carcinoma: A review on epidemiology, current surgical & chemotherapeutic options. In: Lazăr D, editor. Gastric Carcinoma- New Insights into Current Management. Croatia: InTech; 2013.
-
- Ruan K, Song G, Ouyang G. Role of hypoxia in the hallmarks of human cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2009;107:1053–1062. - PubMed
-
- Vaupel P, Mayer A. Hypoxia in cancer: significance and impact on clinical outcome. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:225–239. - PubMed
Publication types
V体育官网 - MeSH terms
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育官网入口" Full Text Sources
"V体育官网入口" Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
"V体育官网" Miscellaneous

