NLRP6 inflammasome orchestrates the colonic host-microbial interface by regulating goblet cell mucus secretion
- PMID: 24581500
- PMCID: PMC4017640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.026
V体育ios版 - NLRP6 inflammasome orchestrates the colonic host-microbial interface by regulating goblet cell mucus secretion
Abstract
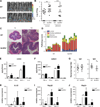
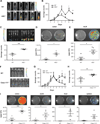
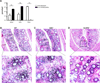
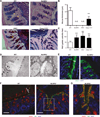
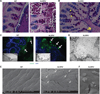
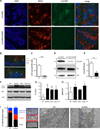
Mucus production by goblet cells of the large intestine serves as a crucial antimicrobial protective mechanism at the interface between the eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells of the mammalian intestinal ecosystem. However, the regulatory pathways involved in goblet cell-induced mucus secretion remain largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate that the NLRP6 inflammasome, a recently described regulator of colonic microbiota composition and biogeographical distribution, is a critical orchestrator of goblet cell mucin granule exocytosis. NLRP6 deficiency leads to defective autophagy in goblet cells and abrogated mucus secretion into the large intestinal lumen. Consequently, NLRP6 inflammasome-deficient mice are unable to clear enteric pathogens from the mucosal surface, rendering them highly susceptible to persistent infection. This study identifies an innate immune regulatory pathway governing goblet cell mucus secretion, linking nonhematopoietic inflammasome signaling to autophagy and highlighting the goblet cell as a critical innate immune player in the control of intestinal host-microbial mutualism VSports手机版. PAPERCLIP: .
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved V体育安卓版. .
Figures (V体育官网)

"V体育ios版" Comment in
-
Is the intestinal goblet cell a major immune cell? (VSports最新版本)Cell Host Microbe. 2014 Mar 12;15(3):251-2. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.014. Cell Host Microbe. 2014. PMID: 24629330 Free PMC article.
-
Mucus, it is not just a static barrier.Sci Signal. 2014 Apr 29;7(323):pe11. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005357. Sci Signal. 2014. PMID: 24782564
VSports注册入口 - References
-
- Artis D, Wang ML, Keilbaugh SA, He W, Brenes M, Swain GP, Knight PA, Donaldson DD, Lazar MA, Miller HR, et al. RELMbeta/FIZZ2 is a goblet cell-specific immune-effector molecule in the gastrointestinal tract. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:13596–13600. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom KS, Guttman JA, Rumi M, Ma C, Bouzari S, Khan MA, Gibson DL, Vogl AW, Vallance BA. Modulation of intestinal goblet cell function during infection by an attaching and effacing bacterial pathogen. Infection and immunity. 2008;76:796–811. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
Substances
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports手机版 - Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

