Dovitinib versus sorafenib for third-line targeted treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial
- PMID: 24556040
- PMCID: VSports最新版本 - PMC5719485
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70030-0
Dovitinib versus sorafenib for third-line targeted treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial
Abstract
Background: An unmet medical need exists for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who have progressed on VEGF-targeted and mTOR-inhibitor therapies. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) pathway activation has been proposed as a mechanism of escape from VEGF-targeted therapies. Dovitinib is an oral tyrosine-kinase inhibitor that inhibits VEGF and FGF receptors. We therefore compared dovitinib with sorafenib as third-line targeted therapies in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma VSports手机版. .
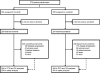
Methods: In this multicentre phase 3 study, patients with clear cell metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received one previous VEGF-targeted therapy and one previous mTOR inhibitor were randomly assigned through an interactive voice and web response system to receive open-label dovitinib (500 mg orally according to a 5-days-on and 2-days-off schedule) or sorafenib (400 mg orally twice daily) in a 1:1 ratio. Randomisation was stratified by risk group and region. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) assessed by masked central review. Efficacy was assessed in all patients who were randomly assigned and safety was assessed in patients who received at least one dose of study drug. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials V体育安卓版. gov, number NCT01223027. .
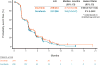
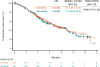
Findings: 284 patients were randomly assigned to the dovitinib group and 286 to the sorafenib group V体育ios版. Median follow-up was 11·3 months (IQR 7·9-14·6). Median PFS was 3·7 months (95% CI 3·5-3·9) in the dovitinib group and 3·6 months (3·5-3·7) in the sorafenib group (hazard ratio 0·86, 95% CI 0·72-1·04; one-sided p=0·063). 280 patients in the dovitinib group and 284 in the sorafenib group received at least one dose of study drug. Common grade 3 or 4 adverse events included hypertriglyceridaemia (38 [14%]), fatigue (28 [10%]), hypertension (22 [8%]), and diarrhoea (20 [7%]) in the dovitinib group, and hypertension (47 [17%]), fatigue (24 [8%]), dyspnoea (21 [7%]), and palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia (18 [6%]) in the sorafenib group. The most common serious adverse event was dyspnoea (16 [6%] and 15 [5%] in the dovitinib and sorafenib groups, respectively). .
Interpretation: Dovitinib showed activity, but this was no better than that of sorafenib in patients with renal cell carcinoma who had progressed on previous VEGF-targeted therapies and mTOR inhibitors. This trial provides reference outcome data for future studies of targeted inhibitors in the third-line setting. VSports最新版本.
Funding: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation V体育平台登录. .
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. VSports注册入口.
Conflict of interest statement (VSports app下载)
Conflicts of Interest: RJM has received research funding from Novartis, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline, has consulted for Bayer and Pfizer, and has provided paid expert testimony for Pfizer. CP has acted as a speaker and/or consultant for Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer Schering, Astellas, AVEO, and Boehringer-Ingelheim and has received research grants from Novartis and Bayer Schering. NJV has consulted for Novartis and Bayer. CNS has received honoraria from Novartis, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline V体育官网入口. CS has been an advisory board member for GlaxoSmithKline, Astellas, Pfizer, and Novartis. CK has received honoraria for presentations from and has consulted and been an advisory board member for Novartis. GAB has received honoraria for CME lectures on RCC and funding for travel to cancer meetings from Novartis. BM has received honoraria for speeches and advisory board meetings from Novartis, Bayer, Pfizer, Roche, and Astellas. UDG has received honoraria as a speaker and/or consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Bayer, and Novartis. VG has received honoraria from Novartis, Pfizer, Astellas, Bayer, Roche, and GlaxoSmithKline and has consulted for Novartis, Pfizer, Astellas, Bayer, and GSK. IDD has chaired GlaxoSmithKline pazopanib (RCC) advisory board (2009), Janssen abiraterone advisory board (2010), and Bayer Asia-Pacific radium-223 dichloride advisory board (2012) and has been an advisory board member for Pfizer RCC advisory board, Novartis RAD001 advisory board, Medivation MDV3100 international advisory board, Bristol-Myers Squibb ipilimumab advisory board, Sanofi Jevtana advisory board, Bristol-Myers Squibb anti-PD1 advisory board, Astellas oncology portfolio advisory board, and Ipsen tasquinimod advisory board. IDD received no renumeration for any of this activity; all payments and honoraria were invoiced by and paid to ANZUP Cancer Trials Group. J-LL has received research funding from Bayer and has consulted for Pfizer, Novartis, Bayer, Sanofi-Aventis, and Astellas. EE has been an advisory board member for GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Novartis with all honoraria directly donated to Fundeso (Fundacion for Cancer Research). GU, CC, MS, MM and MShi are employees of Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. BE has received honoraria for advisory board meetings from Bayer, Pfizer, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, and AVEO. All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
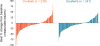
Comment in
-
Third-line dovitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Mar;15(3):245-6. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70082-8. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24556039 No abstract available.
-
"VSports在线直播" Kidney cancer: targeting FGF for third-line treatment of mRCC.Nat Rev Urol. 2014 Apr;11(4):186. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2014.55. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Nat Rev Urol. 2014. PMID: 24595120 No abstract available.
References
-
- Escudier B, Szczylik C, Porta C, Gore M. Treatment selection in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: expert consensus. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9:327–37. - PubMed
-
- Bukowski RM. Temsirolimus: a safety and efficacy review. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2012;11:861–79. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. [accessed December 10, 2013];Kidney cancer version 2.2014. 2013 http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf.
-
- European Association of Urology. Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Bex A, et al. [accessed May 7, 2013];Guidelines on renal cell carcinoma. 2013 VSports手机版 - http://www.uroweb.org/gls/pdf/10_Renal_Cell_Carcinoma_LRV2.pdf.
-
- Presta M, Dell'Era P, Mitola S, Moroni E, Ronca R, Rusnati M. Fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor system in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005;16:159–78. - PubMed
V体育官网 - Publication types
- Actions (VSports手机版)
"V体育安卓版" MeSH terms
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Substances
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Associated data
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
VSports - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

